The Glossopharyngeal Nerve: A Mixed Cranial Nerve Innervating the Throat and Tongue
- 2. Glossopharyngeal • Fibers emerge from the medulla, leave the skull via the jugular foramen, and run to the throat • Nerve IX is a mixed nerve with motor and sensory functions • Motor – innervates part of the tongue and pharynx, and provides motor fibers to the parotid salivary gland • Sensory – fibers conduct taste and general sensory impulses from the tongue and pharynx
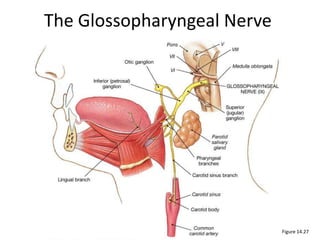
- 3. Glossopharyngeal nerve • Leave the skull through jugular foramen • Passes forwards between internal jugular vein and external carotid artery. • Deep to styloid process. • Between external and internal carotid arteries at posterior border of stylopharyngeus then lateral to it. • Reaches the pharynx by passing between middle and inferior constrictor, deep to hyoglossus, where it breaks into terminal branches. •
- 4. Glossopharyngeal Nerve • A mixed nerve (sensory, motor, parasympathetic) • Emerges from the ventral surface of the medulla oblongata • Runs laterally in the posterior cranial fossa • Leaves the skull by passing through the central part of the jugular foramen • Has superior and inferior ganglia, that are located within the jugular foramen.
- 5. • At its exit from the skull, it passes forward between the internal jugular vein and internal carotid artery, within the carotid sheath • Descends to the lower border of the stylopharyngeus muscle. • Then curves forward around the stylopharyngeus and • Passes through the gap between the superior and middle constrictor muscles of the pharynx
- 6. • Passes under cover of the hyoglossus muscle • Distributed to the: Palatine tonsil Mucous membrane of the fauces and base of the tongue, Mucous glands of the mouth P F T PT
- 7. Gloosopharyngeal nerve • jf--jugular foramen • sg--superior ganglion • ig--inferior ganglion • tp--tympanic plexus • lpn--lesser petrosal nerve • fo--foramen ovale • og--otic ganglion • pg--parotid gland • sp--nerve to stylopharyngeus muscle • pb--pharyngeal branch • ncbcs--nerve to carotid body carotid sinus • Red solid -- motor • Red dotted -- parasympathetic • Yellow -- sensory (afferent)
- 8. Glossopharyngeal nerve • Ganglia • Superior ganglion small, with no branches. • Inferior ganglion, large carries general sensations from pharynx, soft palate and fauces.
- 10. Detail on Glossopharyngeal (IX) Function: •Motor to stylopharyngeus muscle. •Parasympathetic secretomotor fibers to parotid gland. •Sensory to pharynx, tonsils, and posterior 1/3 of tongue. •Taste fibers for posterior 1/3 of tongue.
- 11. Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX) • Innervates structures of the tongue and pharynx Table 14.3 (9 of 12) Facial nerve (VII) Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) Vagus nerve (X) Accessory nerve (XI) Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
- 12. COURSE • It arises from the medulla ,and then passes through the Jugular foramen of the skull ,between the IJV and the ICA. • It is accompanied by Cranial nerves X and XI. • It follows the ICA.
- 13. • It passes under the Styloid process ,and then into the pharynx ,where it lies over the Stylopharyngeus muscle and the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle. • It then passes undercover of the of the Hyoglossus muscle ,and is then distributed to the Palatine tonsil,and mucus memb of fauces,base of tongue ,and mucus glands of the mouth.
- 14. 1. The glossopharyngeal nerve arises by 4-5 rootlets from the posterolateral sulcus of medulla. 2. It leaves the skull through the jugular foramen. 3. While it lies in jugular foramen it has 2 small sensory ganglia (superior and inferior). 4. It descends downwards inside the upper carotid sheath superficial to vagus nerve and between IJV & ICA lying deep to the styloid process and muscle attached to it. 5. Then it leaves the carotid sheath and passes forwards with stylopharyngeus muscle between the ICA & ECA. 6. Ascends deep to hyoglossus to reach the tongue. Termination: it ends into terminal branches supplying the mucous membranes of pharynx, tonsil and the posterior 1/3 of tongue. Course of Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- 15. IX : Glossopharyngeal Nerve : Glossopharyngeal nerve nuclei & their central connections It is a mixed N. ,attached lateral to olive in rostral medulla and leaves the skull through jugular foramen. It receives afferent Fs. From : 1-Receptors of general sensation in pharynx, post.1/3 of tongue, eustachian tube & middle ear. 2- Taste buds of pharynx & post.1/3 of tongue. 3- Chemoreceptors in carotid body & Baroreceptors in the carotid sinus.
- 16. 1. Meningeal branch (sensory): Arises from the intracranial part of the glossopharyngeal nerve. Sensory nerve supplies meninges of posterior cranial fossa. Branches of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- 17. 2. Tympanic branch (Jacobson's Nerve- parasympathetic nerve): Preganglionic parasympathetic nerve to parotid gland. Arises from the inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve in the jugular fossa. Course of the tympanic nerve: It passes through the tympanic canaliculus. It reaches the middle ear cavity where it breaks to form the tympanic plexus. Lesser superficial petrosal nerve arises from the tympanic plexus and reaches the middle cranial fossa. Then lesser superficial petrosal nerve passes through the foramen ovale to reach infratemporal fossa to relay in the otic ganglion. The postganglionic fibers joint the auriculotemporal to supply the parotid gland. Branches of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- 18. 3. Carotid branch (sensory): sensory nerve to the carotid sinus and carotid body. 4. Nerve to stylopharyngeus muscle (motor): motor nerve to stylopharyngeus muscle. Branches of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- 19. 5. Pharyngeal branches (sensory): they enter the formation of the pharyngeal plexus and supplies the mucous membrane of pharynx. The pharyngeal plexus receives also: a. Motor fibers (the pharyngeal branches of vagus nerve). b. Sympathetic fibers(the pharyngeal branches of the superior cervical ganglion) Branches of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- 20. 6. Tonsillar branches (sensory): to the palatine tonsil. 7. Lingual branches (sensory): terminal branches to mucous membrane of the posterior 1/3 rd of the tongue (taste and general sensation). Branches of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- 21. Branches • Tympanic branch: Passes to the tympanic plexus in the middle ear and: Supplies sensory fibers to the plexus Carries preganglionic parasympathetic fibers, that leave the plexus as lesser petrosal nerve and synapse in the otic ganglion • Carotid branch: carries sensory fibers from the carotid sinus & carotid body • Muscular branch to the stylopharyngeus muscle
- 22. Branches cont’d • Lingual branch: passes to the posterior third of the tongue and the circumvellate papillae • Pharyngeal branches: carry sensory fibers to the pharyngeal plexus, which supplies the mucous membrane of the pharynx, tonsil and soft palate • Communicates with the: • Vagus & facial nerves • Superior cervical ganglion of the sympathetic chain
- 23. Branches. • Of communications: • Inferior ganglion and • superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. • Superior ganglion and auricular branch of vagus. • Its trunk and facial nerve at stylomastoid foramen
- 24. Branches. • Of distribution: • Tympanic. • Stylopharyngeus. • Pharyngeal. • Tonsillar. • Lingual .
- 25. IMPORTANT BRANCHES • The Tympanic br.to the tympanic plexus in the middle ear. • Lesser petrosal N arises from this plexus and passes to the parotid gland. • Carotid br,which carries sensory fibres . • Nerve to the Stylopharyngeus • Pharyngeal brs • Lingual br ,which supplies the post 1/3rd of the tongue.
- 26. • C/C The general sensory component mediates the afferent limb of pharyngeal reflex in which touching the back of the pharynx elicits the gag reflex . This is used to test the Glossopharyngeal nerve clinically.
- 27. IX : Glossopharyngeal Nerve Fibres : Glossopharyngeal nerve nuclei & their central connections. Red= motor, brown=parasymp.,blue=sensory 1-Afferent Fs. for general sensation : end in trigeminal sensory nucleus. -Fibres carrying touch sensation from back of tongue +pharynx are important for mediating gag reflex, through connection with nucleus ambiguus & hypoglossal nucleus. 2-Afferent visceral (chemo-& baroreceptors) & taste Fs. : end in nucleus solitarius of medulla.
- 28. IX : Glossopharyngeal Nerve Fibres : Glossopharyngeal nerve nuclei & their central connections. Red= motor, brown=parasymp.,blue=sensory 3-Efferent motor Fibres : arises from its motor nucleus in the rostral part of nucleus ambiguus of medulla to supply stylopharyngeus involved in swallowing. 4-Efferent Parasympathetic Fibres : arises from inferior salivary nucleus of rostral medulla to synapse in otic ganglion, then via post-ganglionic Fs.innervate parotid gland.
- 30. 1. Nucleus ambiguus (SVE) • Branchial motor to stylopharyngeus 2. Inferior salivary nucleus (GVE) • to parotid gland (via otic ganglion)
- 31. 3. Spinal trigeminal nucleus • Somatic sensory from outer ear (superior ganglion of IX) 4. Nucleus of the solitary tract • Visceral sensory from carotid body and sinus, mucosa of pharynx, posterior tongue, middle ear (inferior ganglion of IX) • Visceral sensory from taste buds on posterior third of tongue (inferior ganglion of IX)
- 32. Glossopharyngeal nerve (Ⅸ) Components of fibers • SVE fibers: originate from nucleus ambiguus, and supply stylopharygeus • GVE fibers: arise from inferior salivatory nucleus and ralyed in otic ganglion, the postganglionic fibers supply parotid gland • SVA fibers: arise from the cells of inferior ganglion, the central processes of these cells terminate in nucleus of solitary tract, the peripheral processes supply the taste buds on posterior third of tongue • GVA fibers: visceral sensation from mucosa of posterior third of tongue, pharynx, auditory tube and tympanic cavity, carotid sinus and glomus, and end by synapsing with cells of nucleus of solitary tract • GSA fibers: sensation from skin of posterior surface of auricle and
- 34. Course: leaves the skull via jugular foramen Branches • Lingual branches : to taste buds and mucosa of posterior third of tongue • Pharyngeal branches : take part in forming the pharyngeal plexus • Tympanic nerve : GVE fibers via tympanic and lesser petrosal nerves to otic ganglion, with postganglionic fibers via auriculotemporal (Ⅴ3) to parotid gland • Carotid sinus branch : innervations to both carotid sinus and glomus • Others: tonsillar and stylophayngeal branches Otic ganglion: situated just below foramen ovale
- 38. Glossopharyngeal Nerve • Modalities: SVM: From: Nucleus ambiguous. To: Stylopharyngeus.
- 39. Glossopharyngeal Nerve • Modalities: GVS: From: Carotid body. Carotid sinus.
- 41. Glossopharyngeal Nerve • Modalities: GVM: Preganglionics: From: Inferior salivatory nucleus. To: Otic ganglion. Postganglionics: To: Parotid gland.
- 42. Glossopharyngeal Nerve • Modalities: GSS: From: Posterior 1/3 of tongue. External ear. Middle ear cavity.
- 43. Glossopharyngeal Nerve • Modalities: SVS: From: Posterior 1/3 of tongue (taste).
- 44. Functions • Receives general sensory fibers from the posterior ⅓ of the tongue, tonsil, pharynx, middle ear and carotid sinus. • Receives special sensory (taste) fibers from the posterior ⅓ of the tongue and the circumvellate papillae • Supplies parasympathetic fibres to the parotid gland via the otic ganglion • Supplies motor fibers to stylopharygeus muscle • Contributes sensory fibers to the pharyngeal plexus
- 45. Table 13.2
- 46. Cranial nerves Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Functions: Sensory (general somatic afferent, special visceral afferent, general visceral afferent), motor (special visceral efferent), and parasympathetic (general visceral efferent) for derivatives of the 3rd pharyngeal arch. Nuclei: Four nuclei in the medulla send or receive fibers via CN IX: two motor and two sensory. Three of these nuclei are shared with CN X. The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) emerges from the lateral aspect of the medulla and passes anterolaterally to leave the cranium through the anterior aspect of the jugular. At this foramen are superior and inferior (sensory) ganglia, which contain the pseudounipolar cell bodies for the afferent components of the nerve. CN IX follows the stylopharyngeus, the only muscle the nerve supplies, and passes between the superior and the middle constrictor muscles of the pharynx to reach the oropharynx and tongue. It contributes sensory fibers to the pharyngeal plexus of nerves. CN IX is afferent from the tongue and pharynx (hence its name) and efferent to the stylopharyngeus and parotid gland. Branchial Motor Motor fibers pass to one muscle, the stylopharyngeus, derived from the 3rd pharyngeal arch. Parasympathetic (Visceral Motor) Following a circuitous route initially involving the tympanic nerve, presynaptic parasympathetic fibers are provided to the otic ganglion for innervation of the parotid gland. The otic ganglion is associated with the mandibular nerve (CN V3), branches of which convey the postsynaptic parasympathetic fibers to the parotid gland . Sensory (General Sensory) The general sensory branches of CN IX are as follows : The tympanic nerve. The carotid sinus nerve to the carotid sinus, a baro- (presso) receptor sensitive to changes in blood pressure, and the carotid body, a chemoreceptor sensitive to blood gas (oxygen and carbon dioxide levels). The pharyngeal, tonsillar, and lingual nerves to the mucosa of the oropharynx and isthmus of the fauces (L. throat), including palatine tonsil, soft palate, and posterior third of the tongue. In addition to general sensation (touch, pain, temperature), tactile (actual or threatened) stimuli determined to be unusual or unpleasant here may evoke the gag reflex or even vomiting. Taste (Special Sensory) Taste fibers are conveyed from the posterior third of the tongue to the sensory ganglia.
- 47. Lesion of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve: 1. Loss of taste and general sensation from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue. 2. Loss of sensation in the pharynx. 3. Some pharyngeal weakness. 4. Loss of salivation from the parotid gland.
- 48. Glossopharyngeal Nerve Lesions • Glossopharyngeal nerve lesions produce: Difficulty in swallowing Loss of general sensation over the posterior one-third of the tongue, palate, and pharynx Loss of taste sensation over the posterior one-third of the tongue and palate Dysfunction of the parotid gland Loss of the gag reflex
- 49. The glossopharyngeal nerve is a mixed nerve containing: a. Sensory fibers. b. Parasympathetic fibers c. Motor fibers. It is more important as sensory than as a motor nerve. Origin: from posterolateral sulcus of medulla. The Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
- 50. It has three nuclei: 1. The upper part of nucleus ambiguous: it lies in the medulla (motor function). 2. The inferior salivary nucleus: it lies in the medulla (parasympathetic function). 3. The solitary nucleus: it lies in the medulla (sensory function). Nuclei of Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- 57. IX: GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL • carries information from the head and neck to the brainstem. • Information about blood pressure (baroreceptors)
- 58. CN IX: glossopharyngeal nerve
- 59. CN IX and X
