E commerce full notes for mba
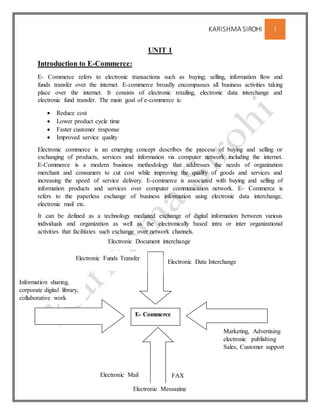
- 1. KARISHMA SIROHI 1 UNIT 1 Introduction to E-Commerce: E- Commerce refers to electronic transactions such as buying; selling, information flow and funds transfer over the internet. E-commerce broadly encompasses all business activities taking place over the internet. It consists of electronic retailing, electronic data interchange and electronic fund transfer. The main goal of e-commerce is: Reduce cost Lower product cycle time Faster customer response Improved service quality Electronic commerce is an emerging concept describes the process of buying and selling or exchanging of products, services and information via computer network including the internet. E-Commerce is a modern business methodology that addresses the needs of organization merchant and consumers to cut cost while improving the quality of goods and services and increasing the speed of service delivery. E-commerce is associated with buying and selling of information products and services over computer communication network. E- Commerce is refers to the paperless exchange of business information using electronic data interchange, electronic mail etc. It can be defined as a technology mediated exchange of digital information between various individuals and organization as well as the electronically based intra or inter organizational activities that facilitates such exchange over network channels. E- Commerce Electronic Funds Transfer Electronic Data Interchange Electronic Mail FAX Marketing, Advertising electronic publishing Sales, Customer support Information sharing, corporate digital library, collaborative work Electronic Messaging Electronic Document interchange
- 2. KARISHMA SIROHI 2 Features of E- Commerce: 1. Payment: enabling credit card, smart card, e-money and other payments along with electronic funds transfer. 2. Service Availability: It automates the conduct of business among enterprises, customers, suppliers and employers anytime, anywhere. 3. Advertising and marketing: publicizing and advertising product and services. 4. Sales: generating orders for the product. 5. Fulfillment: processing the order and delivering product. 6. Support: providing pre and post sale assistant to generate more sales. 7. Inventory Mgt: maintaining and reporting inventory status. 8. Secure communication: fast efficient, reliable communication with customers and partners. 9. E commerce allows you to gather information from customers while delivering a marketing and sales pith through a website. 10. E commerce can be a fully integrated solution or a technical front end to a business that otherwise isn’t wired. Main activities of E commerce Buying and selling of goods Shipping of product Producing financial statement. Goals of E Commerce: Reduce cost Reduced product cycle time Attract more customer Faster customer response Improve service quality Benefits of E- commerce: 1. Benefits to organization: E- commerce decreases the cost of creating, processing, distributing, storing and retrieving paper based information. E commerce reduces the time Improved Image Improved customer service New found business partners. 2. Benefits to consumer: Customer can do transaction 24 hr a day It provides customers with more choices
- 3. KARISHMA SIROHI 3 Functions Transaction Capabilities Service Mgt. Process mgt. Communication Function It allows quick delivery It provides customers with less expensive products and service. Customers can interact with other customer in electronic communication. 3. Benefits to society: It reduces the time for travelling for shopping. It allows some merchant to be sold at low price It enables people in rural areas to enjoy products and services It facilitates delivery of public services, such as health care etc. Functions of E- Commerce: 1. Transaction Capabilities:
- 4. KARISHMA SIROHI 4 Forces fueling E- commerce: Economic Forces Market Forces Technology Forces Categories of E commerce: Business to Business Business to Consumer Consumer to Consumer Consumer to Business Business to Government Government to Business Government to Citizen 1. B2B: Business to business web sites sell the product to the intermediate buyer who takes the products to the final consumer. In this type of web sites a wholesaler places an order through the companies web sites and then sells the supplies to the final consumer as shown in the diagram: 2. B2C: Business to consumer is a website where all transaction take place between a business organization and the final consumer. In this type of websites customer login to the organization’s website and place an order to buy the goods after receiving the order the organization would complete the order and sends the goods to the customer and the customer would receive the ordered goods. Customer Wholesaler Supplies Order Sell Business Org. Order processing Website
- 5. KARISHMA SIROHI 5 3. C2C: In this category consumers sell directly to consumer. If an individual have something to sell, then he get it listed at an auction site, and others can bid for it. For example: at an auction site, customer located in India and in Washington can register. A customer form India places an advertisement on the website. A customer from Washington, while surfing, looks at the advertisement and decides to purchase the product. Thus, the deal is finalized through the web site without an actual meeting. 4. C2B: In such sites, the consumer places an estimate of the amount of money he is willing to spend for a particular service. Businesses that can offer this service within the customer’s specified limit get back to him with the offer. Such sites depend on proper estimate by consumer. Customer Business Orgn. Website Process Order Receives Goods Customer in India Customer in Washington Advertisement Places an advertisement Wants to sell Wants to buy Receives Products Receives Money Business Orgn. Customer Websites Processes Order Places Money for a particular service Receives Products Receives Money
- 6. KARISHMA SIROHI 6 5. B2G: It is a website used by the govt. to exchange information and trade with various organization across the world. 6. G2B: A G2B website is an attempt by the govt. to reached to business. Such sites provides access to various application forms. 7. G2C: A G2C website is an attempt by the govt. to reach out to people in general. The govt. regularly conducts auctions and sales of vehicles, machinery and other material. These auctions are high valued and are visited by customers. These websites also provides access to application forms. Disadvantages of E commerce: Security Training and Maintenance Hardware and Software problem Online Purchasing security Government Website Business Orgn. Business Orgn. Government Website Government Website People/ Customer
- 7. KARISHMA SIROHI 7 Infrastructure of E- Commerce: Here are seven important infrastructure decisions that ecommerce businesses face. 1. Marketing: Of all the infrastructure elements, marketing may be the most important. To succeed, your website must be found. Once visitors are on your site, you need to keep them there and compel them to buy from you. That’s the job of your marketing team. Whether it’s website design, social media, search marketing, merchandising, email, or other forms of advertising, it’s all about marketing. To effectively manage marketing activities in-house is very challenging. Most small ecommerce businesses outsource some element of marketing. 2. Facilities: A key competitive advantage that ecommerce businesses have over brick-and- mortar stores is the investment in their physical offices and warehouses. In many cases, you can host your business out of a home office and your basement or garage. If you drop ship or outsource fulfillment, you may be able to do that for a long period of time. Even when you grow to have many employees, you can set up your offices in class B or C space, as you have no need for a fancy store in the right location. A word of advice is to keep your options flexible. Try to find an office park that has a wide variety of spaces in different sizes. You may be able to start in a smaller space and move up to a larger one without penalty, as your needs change. 3. Customer Service: There are many choices today for delivering high-quality customer service. You can manage those activities in-house or outsource to a third party. Basic customer service for sales and post-sales activities can be handled using email, and by providing an 800 number for more extensive phone support. A customer-management system will make those activities easier, but for smaller companies it is not a requirement. Live chat will impact your operations as someone needs to be available during specified hours of operation. Be sure to gauge the impact of that on your organization, if you decide to handle those activities in house. 4. Information Technology: Choosing the right ecommerce platform is one of the most important decisions you will make in your business. Do you want to build and host your own system, outsource the development and then manage the system going forward, or use a hosted, software-as-a-service platform that is more turnkey and externally managed? If you build and host your own system, you may need more cash upfront and skilled administrators and developers on your staff. By using a SaaS platform, you will not need to host or manage the system in-house, but you may still need web developers on staff. Choosing to outsource the development and hosting will reduce your staffing costs, but you will incur higher costs for any future enhancements or changes to your websites. There are pros and cons to any approach. Just be sure to think through the impacts on both your staffing and your cash flow and bottom line before you move forward. 5. Fulfillment: Another key decision is whether you will manage your own inventory or outsource those activities to a fulfillment house or through drop shipping arrangements with your suppliers. Managing your own inventory will provide you with a high level of control, but you will tie up your cash in inventory, warehouse space, and your own fulfillment staff. In some
- 8. KARISHMA SIROHI 8 industries — like the jewelry supply industry that my previous business was in — managing your own inventory was the most logical choice. We had no alternative for drop shipping, and most items were purchased in bulk and were very small. We did not trust preparation and fulfillment to an outside service. Select the best fulfillment option to meet your needs. Be sure to understand the costs involved and analyze the other options before moving forward. 6. Finance and Administration: As with other business operations, you will need to decide if you want to manage your finance and administration activities in-house, outsource, or a hybrid of the two. If your ecommerce platform is tightly integrated to your accounting system, you may have very little need for an in-house bookkeeper. If you use separate systems for your website, order management and accounting, you may need more help for data entry and making sure that the information is properly managed Many ecommerce companies use outside services for vendor payments, payroll, and other basic accounting activities. They decide to focus on the sales, marketing, and customer service. This allows them to maintain a focus on growing their businesses, instead of paying an internal accountant — or doing that work yourself as the business owner. On the administration side, you need a leadership team and provide direction to them. Good communication is important, whether you have 3 or 100 employees. Whether you choose to be more authoritative or democratic in your management style is up to you. But choose a style and stay consistent. Be sure that everyone understands their roles, as well as the overall business strategies. You may need to adjust your approach as your business evolves. 7. Human Resources: Many small-business owners avoid the human resources function. Recruiting, setting up compensation, maintaining compliance and other HR activities are specialized and time consuming. You may choose to bring the resources in-house to manage those activities, but also evaluate outsourcing them. There are many individuals and agencies well equipped to take on your HR activities. Or Media Technical Human Resource Capital Public Policy Scope of E – Commerce: 1. Linking with D & R 2. Interface with customer 3. Enterprise Management 4. Linking with supplier 5. Global e commerce infrastructure
- 9. KARISHMA SIROHI 9 1. Linking with D &R: Market response Product information and distribution Order fulfillment Account receivable 2. Interface with customer: E-shopping Trading in E market Customer service and sales management Online services Customer information gathering 3. Enterprise management: Product development Logistics and supply chain support HRM Training Accounting Financial Planning 4. Linking with supplier: Product sourcing Product information collection Supplier process management Accounts payable management Purchase process management 5. Global e-commerce infrastructure: Security Digital payment E-banking Legal issues E-market formation Generic Framework for E-Commerce: E-commerce Application Supply chain management Video on demand Remote banking Procurement and purchasing Online marketing and advertisement Home shopping
- 10. KARISHMA SIROHI 10 WWW and E- Commerce: E commerce can be defined as a modern business methodology that addresses the desire of firms, consumer, and management to cut cost while improving the quality of goods and increasing the speed of services. The need for e commerce stems from the demand within the business and government to make better use of computer technology to improve business processes and information exchange both within an enterprise and across organization. In short, e-commerce appears to be an integrated force that represents the digital convergence of 21st century business application and computing technologies. E-commerce Application Services: Public Policy Technical Standard Technical Infrasturcture Business Model Business Services Multimedia Content E-Commerce Electronic Document Interchange Corporate Digital Library E-Publishing E-Messaging EFI EDI E Mail Fax Info. Sharing Collaborative work Marketing Advertisement Sales, customer support
- 11. KARISHMA SIROHI 11 The application services layer of e commerce will be comprised of existing and future application build on a innate architecture. Three distinct classes of e-commerce application can be distinguished as: Customer to business transactions Business to business transaction Intra organizational transaction 1. Application Services C2B B2B Intra organizational 2. Brokerage and data management Order processing Payment scheme 3. Interface layer Software agents, Interactive catalogues Directory support function 4. Secure messaging EDI E mail Remote programming Secure hypertext transfer protocol 5. Middle ware services Compound documents Structured documents 6. Network Infrastructure Wireless cellular Radio PCs WWW as the Architecture The E-Commerce framework outline on the www architecture to provide a human analogy, think on the network infrastructure as the skeleton and web is like a flesh, veins, and skin that shape the human body. Block diagram depicting E-Commerce Architecture:
- 12. KARISHMA SIROHI 12 The architecture is made up of three primary entities: client server, web server, and third party services. The client browser usually interacts with the WWW server, which acts as an intermediary in the interaction with third party services. The client browser resides on the user’s PC or workstation and provides an interface to the various types of content. For instance, if the user retrieves a graphics file from a web server, the browser automatically starts up the graphics file are available-JPEG, GIF, TIFF, BMP, among others. The browser has to be smart enough to understand what file it is downloading and what browser extension it needs to activate to display the file. Browsers are also capable of manipulating local files. Web server functions can be categorized into information retrieval, data and transaction management, and security. The third party service could be other web servers that make up the digital library, information processing tools, and electronic payment systems. E-Commerce and Internet Internet as a Network Infrastructure: The internet is the most well known component of information superhighway network infrastructure. Today, the internet is an information distribution system spelling several continents. In very general infrastructure targets not only one electronic commerce applications such as video on demand or home shopping but a wide range of computer based services such as e-mails, EDI, information publishing, information retrieval and video conferencing. Network making up Internet:
- 13. KARISHMA SIROHI 13 This diagram captures the distinction between Academic and Business Internet. Academic Internet consists of various government network, regional networks, campus network, and some international networks. These include NSFNET the premier group of research IP networks in the United States; EBONE the European group of IP networks; and more recently, private IP network run by for profit organizations. The business internet consists of on line services, value added networks, and other e mail only services. The academic and business networks can talk to each other through language translators, called gateways, stationed at the network border. In the past, because only mail gateways were widely implemented and deployed, the most interoperable application or the least common denominator for the entire internet was electronic mail. 6 stages of Internet Growth: The incredible growth of the internet can be divided into 6 stages: 1. Experimental networking (ARPANET, 1965) 2. Discipline specific research (CSNET, MILNET, 1981-85) 3. General research networking ( early NSFNET – 1985-1991) 4. Privatization and commercialization ( present NSFNET) 5. Restricted public data networks for research and education ( NREN) 6. National information infrastructure ( I-Way) The first stage, experimental networking, covers the early years under the aegis of the DOD ARPA and the province of a relatively small technical community. That group developed not only the technology but the cooperative mechanism that made it possible to scale and allow further innovation to occur. The second stage, discipline specific research (1980-1985), grew out of the more general ARPANET and began to build international online communities. CSNET, for instance, linked computer science researchers from all over the world. The third stage, general research networking (1985-1991) and called the NSFNET program, unfolded following the explosive growth in the mid 1980’s. the NSFNET program was established chiefly to allow exchange of information and access to remote resources within the research and education community. Since the backbone network was launched, its traffic has doubled each year and its transmission capacity has increased more than thirtyfold to 45 million bits per second. The fourth stage, privatization and commercialization( 1991-present), involves removing government subsidies to regional networks and dismantling the barriers imposed by restricted acceptable usage policies. The network extends far beyond the research community and today supports not only the expanding backbone services, but also commercial transactions and extensive connections for commercial organizations. The fourth stage recognizes the changing nature of the networking marketplace.
- 14. KARISHMA SIROHI 14 E-Commerce and Internet: e-commerce is the buying and selling of products, information and services over the internet. E business on the other hand represents the transformation of organization business and functional process through the application of technologies, philosophies and computing paradigms of new digital economy. E commerce includes: Merchandise planning and tracking Order entry and tracking Order fulfillment Warehousing Inventory management Shipping Returns Other logistics Pricing and promotion Financial accounting and reporting Customer services Customer relationship management Knowledge management Supply chain management Further, the internet apart from enabling e-commerce is also contributing to the rapid internationalization of services sector. It makes this to happen to unbundle consumption of information intensive service activities like- Computing Accounting Personnel Marketing Distribution. Electronic payment system: EPS are becoming central to online business process innovation as companies look for ways to serve customers faster and at lower cost. The most important function of e-commerce over the I way. As e-commerce involves the exchange of some form of money for goods and services, payment system are integral part of electronic commerce system. Because of the online transactions in electronic commerce, there is a rising concern for the security of these systems.
- 15. KARISHMA SIROHI 15 EPS is also known as EFT, which is defines as any transfer of funds initiated through an electronic terminal, telephone instrument, computer or even magnetic tape to order, instruct or authorized a financial institution to debit or credit of an account. Work on EFT can be categorized on three broad categories: Digital Token Based Payment System: New forms of financial instruments called electronic tokens in the handled in the form of electronic cash or checks. E-tokens are designed as electronic analogue of various forms of payment backed by a bank or financial institution, basically they are equivalent to cash that is assured by a bank. Electronic tokens are of three types: 1. E-cash or real time: electronic commerce transactions are settled with the exchange of electronic currency. Such as e-cash. 2. Prepaid or debit card: in this case, consumers need to pay in advance for the privilege of getting information. 3. Postpaid or Credit card: this is another option available, where the server authenticates the consumer and verifies with the bank that funds are adequate before purchase. Electronic Cash: it is a new concept in online payment systems because it combines computerized convenience with security and privacy that improve on paper cash. It can be based on e-payment protocol that supports a series of payment transactions using electronic tokens or coins issued by third party. There are three types of users in this payment system: the payer e.g. consumer Category Banking and Financial Payment •Large scaleor wholesalepayment •Small scaleor retail payment •Home payment Retailing Payment •Debit Card •Credit Card •Charge Card Online electronic commerce payment •Token Based Payment system •---e-cash •--e-checks •--smart card and debit cards •Credit Card Payment System •----encrypted credit card •---third party authorization numbers
- 16. KARISHMA SIROHI 16 a payee e.g. merchant a financial network where both the payer and payee have accounts. There are three types of transactions in this payment system as given below: Withdrawal: the payer transfers some money from his bank account to his or her payment card. Payment: the payee transfers the money from the card to the payee. Deposit: the payee transfers the money received to his bank account. There are two types of implementations of this system as given below: Online Payment: the merchant calls the bank and verifies the validity of the consumer’s token or electronic coin before accepting the payment and delivering the merchandise. Offline payment: the merchant submits the consumer’s payment for verification and deposit sometimes after the payment transaction is completed. There are three participants involved in this system as given below: Client wallet software: e-cash software should be installed on the client computer from where the consumer can use e-coins to make purchases from the merchants. The client can store the coins in the client wallet, withdraw coins from that and request new coins from the bank. Merchant software: there has to another merchant software installed on the merchant machine to accept and process payments and sell items. This software will interact with the bank to perform validation and authentication. Also the software can make refunds, if required. Banks: both the client and merchant should have e-cash account in the bank. The bank can issue new coins to the client, validate the coins when presented.
- 17. KARISHMA SIROHI 17 Electronic checks: e-checks are another form of electronic token. They are designed to accommodate the many individuals and entities that might prefer to pay on credit or through some mechanism other than cash. In e-check buyer must register with a third party account server before they are able to write electronic checks. The account server also acts as a billing service. The registration procedure can vary depending on the particular account server and may require a credit card or a bank account to back the checks. Once registered, a buyer can then contact sellers of goods and services. To complete a transaction, the buyer sends a check to the seller for a certain amount of money. These checks may be sent using e mail when deposited. The check authorizes the transfer of account balances from the account against which the check was drawn to the account to which the check was deposited. Smart cards and EPS: in the meantime, thousands of would be sellers of electronic commerce services have to pay one another and are actively looking for payment substitutes. One such substitutes is the smart card. Smart cards have been in existence since the early 1980’s and hold promise for secure transactions using existing infrastructure. Smart cards are credit and debit cards and other card products enhanced with microprocessors capable of holding more information than the traditional magnetic stripe. Relationship based products are expected to offer consumers far greater options, including the following: Access to multiple accounts, such as debit, credit, investments or stored value for e-cash, on one card or an electronic device. A variety of functions, such as cash access, bill payment, balance inquiry, or funds transfer for selected accounts.
- 18. KARISHMA SIROHI 18 Multiple access options at multiple locations using multiple device types, such as an automated teller machine, a screen phone, a personal computer, a personal digital assistant. Credit card and EPS: to avoid the complexity associated with digital cash and electronic checks, consumers and vendors are also looking at credit card payments on the internet as one possible time tested alternative. There is nothing new in the basic process. If consumers want to purchase a product or service, they simply send their credit card details to the service provider involved and the credit card organization will handle this payment like any other. We can break credit card payment on online networks into three basic categories: Payments using plain credit card detail: the easiest method of payment is the exchange of unencrypted credit cards over a public network such as telephone lines or the internet. The low level of security inherent in the design of the internet makes this method problematic. Authentication is also a significant problem, and the vendor is usually responsible to ensure that the person using the credit card is its owner. Without encryption there in so way to do this. Payments using encrypted credit card details: it would make sense to encrypt your credit card details before sending them out, but even then there are certain factors to consider. One would be the cost of a credit card transaction itself. Such cost would prohibit low value payments by adding costs to the transactions. Payments using third party verification: one solution to security and verification problems is the introduction of a third party: a company that collects and approves payments from one client to another. After a certain period of time, one credit card transaction for the total accumulated amount is completed. Encryption and credit cards: encryption is simply when credit card information is entered into a browser or other electronic commerce device and sent securely over the network form buyer to seller as an encrypted message. To make a credit card transaction truly secure and nonrefutable, the following sequence of steps must occur before actual goods, services, or funds below: 1. A customer presents his or her card information securely to the merchant. 2. The merchant validates the customer’s identity as the owner of the credit card account. 3. The merchant relays the credit card charge information and signature to its bank or online credit card processors. 4. The bank or processing party relays the information to the customer’s bank for authorization approval.
- 19. KARISHMA SIROHI 19 5. The customer’s bank returns the credit card data, charge authentication, and authorization to the merchant. Third party processor and credit cards: in third party processing, consumers register with a third party on the internet to verify electronic micro transactions. Verification mechanism can be designed with many of the attributes of electronic tokens, including anonymity. They differ from electronic token systems in that (1) they depend on existing financial instruments and (2) they require the online involvement of at least one additional party and, in some cases, multiple parties to ensure extra security. OTPPs have created a six step process that they believe will be a fast and efficient way to buy information online: 1. The consumer acquires an OTPP account number by filling out a registration form. This will give the OTPP a customer information profile that is backed by a traditional financial instrument such as a credit card. 2. To purchase an article, software, or other information online, the consumer requests the items from the merchant by quoting her OTP account number. The purchase can take place in one of two ways: the consumer can automatically authorize the merchant via browser setting to access her OTPP account and bill her, or she can type in the account information. 3. The merchant contacts the OTPP payment server with the customer’s account number. 4. The OTPP payment server verifies the customer’s account number for the vendor and checks for sufficient funds.
- 20. KARISHMA SIROHI 20 5. The OTPP payment server sends an electronic message to the buyer. This message could be an automatic WWW form that is sent by the OTPP server or could be a simple e mail. The buyer responds to the form or e mail in one of three ways: yes, I agree to pay; no I will not pay; or fraud, I never asked for this. 6. If the OTPP payment server gets a YES from the customer, the merchant is informed and the customer is allowed to download the material immediately.
- 21. KARISHMA SIROHI 21 UNIT 2 E Commerce and Banking: The role of e-commerce in banking is multifaceted impacted by changes in technology. Rapid deregulation of the emergence of new banking institution and basic economic restructuring. Many banks feel that in order to be a profitable they need to reduce operating expenses and maintain strict cost control. This philosophy is evident in many mergers and acquisition occurring in the banking industry. So, the challenge behind bank restructuring lies in adequately operationalizing the motion of cost control. Changing dynamics in Banking Industry: There are 5 distinct factors contribute to the new competitive environment: 1. Changing consumer needs driven by online commerce. 2. Optimization of branch networks in order to reduce cost. 3. Changing demographic trends and potential new consumer market. 4. Cross industry competition caused by de-regulation. 5. New online financial products. 1. Changing Consumer Needs Consumer requirements have changed substantially in the last decade customers want to access account related information download account data for use with personal software products, transfer funds between accounts, and pay bills electronically. Of course, along with these services, banks must be able to supply/guarantee the privacy and confidentiality that customers demand which is not a trivial matter to implement on the part of the banks. Many consumer requirements are based on simple premise customers and financial institutions both seek closer and more multifaceted relationships with one another. Customers want to be able to bank at their convenience, including over the weekend or late at night. Bankers want more stable and long term relationships with their customers. Electronic banking provides a method of communication that will enable the bank customer to be reached served, and sold products and services in their homes and offices whenever it is convenient for them twenty four hours a day, seven days a week. 2. Cost Reduction The central goal of most mergers is to reduce operating costs. During the decade 1984- 1994, the number of banks in the United States fell by 27 percent. In general brick and mortar branches cost at heavy. Online technology can deliver services far more economically than these existing methods as the infrastructure costs such as PC’s are shared with the consumer. As banks merge to reduce their operating costs, they are obviously growing in size. however, even their increased size is dwarfed by many of their new competitors. If banks are going to compete with these larger competitors, they are going to have to address
- 22. KARISHMA SIROHI 22 their traditional banking overhead structures, as well as their existing retail strategies. Providing online financial services can address both these needs. 3. Demographic Trends Consumers are increasingly careful about their personal finances. Social demographic and economic changes have altered the way value their time and money. People spend more time working than ever before, and therefore place a higher premium on their leisure time. Thus, they are a very receptive audience for time saving products and services. In addition, the reduced level of job security and the need to plan for the future has heightened concern over personal debt, retirement planning, tax planning , and saving for college. The companies that take advantage of this opportunity by targeting the appropriate customers with appropriate products and services will have a lasting competitive advantage. As it prov8ides convenience and the ability to customize products and services on a mass level electronic delivery of these products and services will be one of the key means of achieving this advantage. 4. Regulatory Reform Banks occupy a unique strategic position as they act as intermediaries in redistributing capital from areas of excess to areas of scarcity. This role has made financial services a closely watched and regulated industry as government is intersted in the control and stability of this redistribution. Recent years have brought about far reaching regulatory changes that have removed many of the competitive protections banks enjoyed for a long time. The ability to provide complete financial services is necessary if commercial banks are to survive increasing competitive from mutula funds, brokerage firms, and insurance companies. 5. Technology based financial Services Products The growing importance of computer technology is another factor complicating predictions about the future structure of baking. Some observers believe that additional development of electronic cash, such as smart cards, could stimulate further baking consolidation. They point to the fact that the start-up costs associated with electronic payments technology cab be high in part because electronic cash requires large investments in computer software and other resources to establish a network of secure electronic transaction. The development of electronic banking might actually increase competition in banking markets and lower bank operating costs. Electronic banking offers an inexpensive alternative to branching to expand a bank's customer base and many banks are using electronic banking to increase service to their customers. Many banks have started web sites on the internet, and many plan to offer banking services over the internet. Some banks are laready offering certain banking services over the telephone. Smart cards and other forms of electronic cash could be the key to consumer acceptance of home banking, eventually allowing banks to reduce the number of their physical branches.
- 23. KARISHMA SIROHI 23 Home banking industry: Financial institutions work interested in turning the home banking concept into reality as early as 1970. Many banks invested million of dollars in R&D in Oct. 1981. The American banker had a set of articles promoting the virtue of home banking. In 1980’s cable television was considered as possible medium of home banking and telephones was considered in 1970’s. Success of home banking: There are several factors that lead to believe that home banking has a good chance of success these time. 1. Consumers up the learning curve. 2. Increasing consumer awareness. 3. The alternative is too expensive. 4. Huge competition. There are several factors that lead us to believe that home banking has a good chance at success this time. Consumers Up the Learning Curve Consumers are becoming increasingly cornputer- literate and are able to interact more fluently with their online financial service providers. C)ver the years, consumers have demonstrated a high level of acceptance of basic electronic services. The banking industry expects that PCs will eventually replace ATMs and POS terminals as the crucial method of consumer-bank interfacing. However, the use of technology is not just restricted to ordinary consurner-bank interface (or retail banking). Evidence indicates that banks and software companies are begin- ning to find a receptive audience among PC users wanting to simplify bill paying, cheekbook balancing, and tax-related tasks. Increasing Consumer Awareness Advertising about and media attention to online banking have never been stronger. Mainstream magazines are in- creasing the amount of coverage given to computer-related topics. As a result, consumers are increasingly aware of alternatives to traditional branch bank- ing. As consumers become aware of alternatives, they are going to demand more. Banks that fail to meet expectations face the possibility of mass exodus. Large Base of Installed PCs Finally, there is a critical mass of PC-using households with modems. For a long time, home banking was a classic .chicken or egg" ptoblem;
- 24. KARISHMA SIROHI 24 without a large enough sample of potential users, there was no urgency for financial institutions to provide sen-ices. Conversely, without a wide array of services, there was little consumer in- terest. This problem is resolving itself. Today there are more than 30 million PCs in American homes, and, for the first time in history, consumers are now spending more on PCs than TV sets. Modem penetration into house- holds is a key issue for home banking, as online services require a modem. Clearly the technology exists to make home banking a reality. "lether'it will happen via the Intemet, a proprietary service, or both is yet to be deter- mined, but the home banking infrastructure is in place. Home banking implementation approaches: 1. Proprietary bank dial up services. 2. Off the shelf home finance software. 3. Online services based banking 4. www based banking services. Pushed by growing consumer demand and the fear of losing market share, banks are investing heavily in. home banking technology. Collaborating with hardware, software, telecommunications, and other companies, banks are introducing new ways for consumers to access their account balances, transfer funds, pay bills, and buy goods and services without using cash, mailing a cheek, or leaving home. The four major categories of home banking (ii-t historical order) are: Proprietary bank dial-up services. A home banking service, in cornbina on with a PC and modem, lets the bank become an electronic gateway to customers' accounts, enabling them to transfer funds or pay bills directly to creditors accounts. Off-the-shelf home finance software. This category is a key player in cementing relationships between current customers and helping banks gain new customers. Examples include Intuit''s Quicken, Microsoft Money, and Bank of America's MECA software. This software market is attracting interest from banks as it has steady revenue streams by way of upgrades and the sale of related products and services. Online services-based banking. This category allows banks to set up re- tail branches on subscriber-based online services such as Prodigy, CompuServe, and America Online. World Wide Web-based banking. This category of home banking allows Pt,Mbanks to bypass subscriber-based online services and reach the customer's browser directly through the World Wide Web. Ue advantages of this model are the flexibility at the back- end to adapt to new online transaction processing models facilitated by electronic commerce and the el~atiort of the constricting, intermediary (or ordine service). In contrast to packaged software, which offers a limited. Set of services, the online and WRWW approach offers further opportunities. As consumers buy more and more in eyberspace using credit cards, debit cards, and newer financial instruments such as
- 25. KARISHMA SIROHI 25 electronic cash or electronic checks, they need software products to manage these electronic transactions and reconcile them with other off-line transactions. In the future, an increasing number of paper-based, manual financial tasks may be performed electroni- cally on machines such as PCs, handheld digital computing devices, inter- active televisions, and interactive telephones, and the banking software must have the capabilities to facilitate these tasks. E- Commerce and Retailing: Retailing is expected to change with a rapid development of new online sales and distribution channels that literally used from anywhere, anytime from work, school and a hostel, car or airplane. These developments should base impact resulting as much as the catalogue retailing and T.V. based home shopping at most every retailer is re evaluating every aspect of its operations from customer service to adversely merchandising to store designing and logistics to order fulfillment. However, retailer needs to consider the following issues and developing a business order. 1. Product 2. Software interface issue 3. Process 4. Payment issues 5. Market penetration issues. Changing retail industry dynamics: So, the important factors affected retail industry: 1. Over building and excess supply 2. Change in consumer demographics. 3. Change in consumer behavior 4. Technology improvement. Online retailing success stories: 1. PEA POD’s experience 2. CVC international 3. Web based travel agencies. Business problem Solution Requirement Benefits. Open Vs Closed Model: An open system such as web offers two additional key benefits:
- 26. KARISHMA SIROHI 26 Control of user interface Intermediation With a open system the bank designs the user interface and therefore able to incorporate its own look and feel. The authority allows the bank to enhance its brand awareness and maintain direct access to its customer. The open system also allows bank to offer an expended array of financial services and to choose their business partners when offering additional services such as brokerage accounts and mutual funds which leads to stronger customer relationship and increased revenue. Close system: In this system using proprietary financial management software such as Quicen, the software firm act as a intermediary between the bank and its customer. In managing the customer relationship the software provider controls the interface design, thus diminishing and even eliminating any reference to the bank itself. This software provider also control the selection of financial providers and determine the choice of services and availability of those services. Consumer merchandise model: customer service receipt of product authorization of payment placement of order placement of terms negotiation of terms comparison shopping and product selection based on various attributes Product/ service search and discovery of information
- 27. KARISHMA SIROHI 27 UNIT 3
- 28. KARISHMA SIROHI 28 UNIT 4 Intranet and corporate finance: The competitive business environment is forcing firms to re-engineering financial management process. General ledger system and spread sheets (traditional method) prove inadequate when data is voluminous and worldwide, when corporate structure change because of mergers and acquisition and when timely and reliable consolidation, budgets and forecasts are essential. In this section, we provide the setting by elaborating on what financial information system are intended to accomplish. What exactly is financial system: a financial system encompasses business process, procedure, control and data dedicated to operations and maintenance of corporate financial objectives. It incorporates the following tasks: Report and analyses the financial data Simply the budgeting and forecasting process. Enabling better planning Control the financial consolidation of actual results. Answer at ad hoc requests efficiently. Improve cost control and performance measurement. Financial accounting activities: It includes: 1. Processing, maintaining, collecting, transmitting and reporting data about financial event. 2. Supporting financial plan and preparing budget 3. Supporting the preparation of financial statement. Management accounting activities: It includes: 1. Reporting historical transaction to external parties. 2. Accumulating and reporting false information. 3. Safeguarding the asset of company. 4. Providing insight with respect to the value of future transaction. Financial intranet: Accounting software provided a way to enter transactions and manage those transaction in the form of an accounting trial. Today there is a lot more that the business manager’s need from the information lock inside the accounting databases. The information is there but it is very difficult to obtain. Intranet can play a big role in solving this problem because this will allow the
- 29. KARISHMA SIROHI 29 integration necessary to provide accounting information that the manager needs in the specific form they need, when they need it and where they need it. Business problem: 1. Managing information about monthly progress towards annual goals of an organization. 2. Allowing managers to spend time in manipulating not gathering the data. Intranet solutions: Create a central database of measurement information using the web. Requirement use the web for end user interface. Give user easy to use form for query information. Use a data warehouse to store information Generic modules in a financial information system/ understanding the different software models: It includes: 1. General ledger 2. Accounts payable 3. Accounts receivables 4. Asset management 5. Costing 6. Billing and invoicing Intranet and transaction accounting: Intranet offer companies new tools that harness the power of network computer. For the transaction accounting purposes. This includes: 1. Efficient transaction entry 2. Common transaction processes 3. Consistent internal controls 4. Audit trials Payment system/ management: Today’s competitive world demands operational efficiency with strong management control tight integration of purchasing, payables and receivables is necessary to eliminate paper work redundant data entry. The goal is to use automatic price order creation, automatic text with holding and automated voice and payment processing to improve operational efficiency. In this process, the company is linked with supplier and distributor so, the payment can be send and received through e-commerce. This allows customer order to be build after shipment with invoice printed and inventory, sales and accounting information maintain automatically.
- 30. KARISHMA SIROHI 30 Treasury and cash management: The global market place demands support for multiple currency, international tax method and other global business practices. Companies must work with financial institution to boost their ability to deal on global basis. The goal is to enable global companies to manage their money in various foreign exchange accounts. This includes multinational, multi currency bank reconciliation and cash management. In general cash management is to access information related to their checking accounts in order to make timely payment and reduce their exposure to check fraud. Therefore, cash management requires rapid transfer of information between bank and its customer. Human resource management system: HR department are finding that the web is an effective vehicle to deliver more strategic programs and services and to enable line managers and employees to directly access the information and initiate self service transaction. The intranet and web also provide a common, enterprise wide platform to deliver solutions to support a wide range of HR functions including recruiting and application tracking, organization training and development skills planning and performance evaluation compensation and benefit administration etc. HRMS function: Human resources Recruiting Training and development Health and safety Payrolls Payroll calculation Time reporting Tax computation Benefit administration Pension programs Automated enrollment Com X Bank X Bank Y Comp. Y Transfer of funds
- 31. KARISHMA SIROHI 31 Health care benefit management Dental insurance Medical insurance Vision insurance Size and structure of financial software market: Companies are looking for system flexibility to meet changing business requirements such as corporate re-engineering, new govt. reporting requirements, new product line and the ability to link financial data throughout the enterprise. To meet the management needs of large corporations, e commerce solutions are being used to develop and integrated enterprise suite that enables the re-design of financial and accounting processes. Corporate digital library: Today most internal e-commerce system whether centralized or dispersed, concentrate on business transaction data. This focus is essential and few companies of any size can keep pace without automating routine transaction. These transactions affect the key strategic decision strategic and operational decisions are the life blood of every organization. In fact, it is safe to speculate that the next wave of internal commerce will be aimed at decision support. Dimensions of internal e-commerce system: Digital library layer: many corporations are finding that the most effective way to manage their business information is through a corporate library that provides the architecture to model, map, integrate, condense, and transform scattered information housed in digital documents and legacy databases into meaningful business information. Today, the term digital library is widely used as the generic term for diverse information structures that provide organizations and workers access to the vast amount of internal information encoded in multimedia formats. It creates a unified repository of consistent business data for information processing. Digital libraries are of two types: electronic document based digital libraries and structured data or database oriented warehouses. Document digital library: the term document denotes all nondata records, including books, reports, paper materials, electronic files, video and audio. A document digital library is simply, a distributed network of interlinked information that is tailored for electronic publishing. It encompasses new types of information resources; new approach to acquisition; new methods of storage and preservation; new approaches to classification and cataloging; new modes of interaction with information; and shifts in organizational practices. Data warehousing: it is designed as central information repositories for combining and storing vast amounts of historical and reference data from a number of different sources. These corporate data sources include mainframe databases, client-server relational databases, spreadsheets, text reports, flat files, and proprietary systems. A data warehouse is a physical separation of an organization’s operational data systems from its decision
- 32. KARISHMA SIROHI 32 R&D engineering Manufacturing and production accounting and finance documentation manual and records suppliers service and support sales and marketing customer stakeholder human resources govt. regulation legal cases and controls DocumentImaging ( scanning documents for storageandfaxing) structuring documents (structuring and encoding info. using document encoding standards) distributionhypertext ( structuring interlinked textual andmultimedia info.for distributednetwork access) active or compound documents (structuring applications arounda documentinterface) support system. It includes a repository of information that is built using data from the far-flung and often departmentally isolated systems. Making a business case for a document library: This section highlights the role that documents plays in today’s organization and explores how businesses can better meet their customer’s need by improving document management support. Corporate digital library as a core of documentation:---------- Document management describes a wide variety of disparate functions including document authoring and scanning, repository archiving, document distribution and delivery, document processing along the work flow, information search and retrieval, and document browsing or viewing. In this diagram and information architecture that ties different departments around a corporate document library of information that enables cross functional information sharing. This is brought about by establishing information architectures that enable the seamless movement of information across the enterprise networks. Types of digital documents: 1. Document imaging: document imaging emulates microfiche and microfilm. An imaging system passes a paper document through a scanner that renders it digital and then stores the digital data as a bit mapped image of the document. Keyword for each document that help in
- 33. KARISHMA SIROHI 33 indexing and retrieval are entered during scanning. The problem with the imaging approach is that the output contains only images, not encoded text. Consequently, searching the text of a document’s image is possible only using the keywords that categorize that document. The following imaging standards are prominently used: TIFF (tag image file format)- format for interchange of bit-mapped images. It was developed through an industry effort initiated by Aldus Corporation and has achieved de facto standard status. ITU-TSS (international telecommunication union- telecommunication standardization sector)- group Corporate digital library as a core of documentation .6 Facsimile. This standard is used for compression and exchange of bit mapped files. 2. Structured documents: it apply database structuring capabilities to individual documents and documents collections to allow tools to manipulate document content just like fields within database tables. A large array of standards and products are available to help create and manage structured documents, depending on the goal and task at hand. If document interchange between platform and fidelity to document format is the main concern, a compound document architecture may suffice. Standard generalized markup language (SGML) Office document architecture (ODA) Compound document architecture (CDA) Rich text format (RTF) 3. Hypertext documents: hypertext is a way of making document based information more mobile. Mobility of information is necessary for the following reasons: Information in enterprise is seldom located on one node or server but is distributed throughout the organization. Accessing and retrieving large monolithic documents is time consuming. Reuse of document fragments for composing new documents is more effective when information stored on individual systems and servers across an enterprise can be accessed from remote locations. 4. Active documents: it represents what is known as document oriented computing. Active documents provide and interactive interface where all documents, applications, and data related to a particular task are assembled, arranged, and interlinked in such a manner that the user can focus on the task at hand and be shielded from nontask related issues like access, storage, data formats, location, computing or delivery mechanism. Intelligent Agent:
- 34. KARISHMA SIROHI 34 UNIT 5 E-Commerce scenario in Indian corporate: • India has an internet user base of about 354 million as of June 2015. Despite being third largest user base in world, the penetration of e-commerce is low compared to markets like the United States, United Kingdom or France but is growing much faster, adding around 6 million new entrants every month. • In India, cash on delivery is the most preferred payment method, accumulating 75% of the e-retail activities. • As of Q1 2015, seven Indian e-commerce companies have managed to achieve billion- dollar valuation. Namely, Flipkart, Snapdeal, InMobi, Quikr, Amazon India, OlaCabs, and Paytm. Key driver: • Large percentage of population subscribed to broadband Internet, burgeoning 3G internet users, and a recent introduction of 4G across the country. • Explosive growth of Smartphone users, soon to be world's second largest smart phone user base. • Rising standards of living as result of fast decline in poverty rate. • Availability of much wider product range Usage and advantages: • Global Trade • Virtual Businesses • Lower search costs • Increased power of downstream players • No Standing in Queues or Being Placed on Hold Forever • Easier to Compare Prices • Lots of Choices Infrastructure problems: • Payment Collection: When get paid by net banking, one has to end up giving a significant share of revenue (4% or more) even with a business of thin margin. • Logistics: Businesses have to deliver the product, safe and secure, in the hands of the right guy in right time frame.
- 35. KARISHMA SIROHI 35 • Taxation • Cyber crime in E – Commerce Consumer’s attitude: • Consumer attitudes are a composite of a consumer’s • beliefs about • feelings about • behavioral intentions • Beliefs: A consumer may hold both positive beliefs toward an object (e.g., coffee tastes good) as well as negative beliefs (e.g., coffee is easily spilled and stains papers) • Affect: Consumers also hold certain feelings toward brands or other objects. For example, an extreme environmentalist may believe that cutting down trees is morally wrong, but may have positive affect toward Christmas trees because he or she unconsciously associates these trees with the experience that he or she had at Christmas as a child. • Behavioral Intention: The behavioral intention is what the consumer plans to do with respect to the object (e.g., buy or not buy the brand). As with affect, this is sometimes a logical consequence of beliefs (or affect), but may sometimes reflect other circumstances -e.g., although a consumer does not really like a restaurant, he or she will go there because it is a hangout for his or her friends Growth prospects: • OPPORTUNITY FOR RETAILERS • OPPORTUNITY FOR WHOLE SALERS/DISTRIBUTER • OPPORTUNITY FOR PRODUCERS • OPPORTUNITY FOR PEOPLE
