Imaging of the scrotum
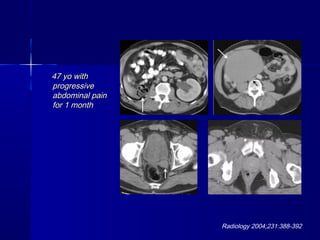
- 1. 47 yo with47 yo with progressiveprogressive abdominal painabdominal pain for 1 monthfor 1 month Radiology 2004;231:388-392
- 2. 25 y/o with mass on imaging
- 3. Imaging of the ScrotumImaging of the Scrotum and Testesand Testes Jud Gash, MDJud Gash, MD
- 4. OutlineOutline AnatomyAnatomy ImagingImaging Testicular MassesTesticular Masses Testicular TorsionTesticular Torsion Scrotal TraumaScrotal Trauma Inflammatory DiseaseInflammatory Disease Extratesticular PathologyExtratesticular Pathology MiscellaneousMiscellaneous
- 6. Scrotum - AnatomyScrotum - Anatomy ScrotumScrotum layers of fascia, muscle andlayers of fascia, muscle and connective tissueconnective tissue Tunica VaginalisTunica Vaginalis – visceral and parietal layersvisceral and parietal layers – potential space around thepotential space around the testestestes Tunica AlbugineaTunica Albuginea – thick layer of fascia investingthick layer of fascia investing the testesthe testes – Along the posterior surface ofAlong the posterior surface of the testis, the tunica albugineathe testis, the tunica albuginea thickens to form thethickens to form the mediastinummediastinum – The mediastinum projectsThe mediastinum projects inward into the testisinward into the testis
- 7. Testes –Testes – Embryology andEmbryology and AnatomyAnatomy TestesTestes – 2X3X5 cm2X3X5 cm – mediastinummediastinum contain rete testis - spermcontain rete testis - sperm containing channelscontaining channels – Appendix of testesAppendix of testes Mullerian duct remnantMullerian duct remnant EpididymisEpididymis Attatched to posterolateral testisAttatched to posterolateral testis head, body and tailhead, body and tail Appendix of the head and tailAppendix of the head and tail paradidymisparadidymis Spermatic cordSpermatic cord vas, artery, veins and lymphaticsvas, artery, veins and lymphatics Note: testicular lymphatics drainNote: testicular lymphatics drain to paraaortic; while scrotum toto paraaortic; while scrotum to inguinalinguinal
- 8. Testes - HistologyTestes - Histology Connective tissueConnective tissue frameworkframework – tunica albugineatunica albuginea – mediastinum testismediastinum testis – septa which divide the organ into lobules.septa which divide the organ into lobules. Within theWithin the lobulelobules, the seminiferouss, the seminiferous tubules produce sperm. Thetubules produce sperm. The seminiferous tubulesseminiferous tubules consist of germconsist of germ cells and Sertoli cells.cells and Sertoli cells. – Germ cells (spermatogonia,Germ cells (spermatogonia, spermatocytes, etc) -spermatocytes, etc) - develop into spermatozoadevelop into spermatozoa – sertoli cells - supporting cellssertoli cells - supporting cells Between the tubules, theBetween the tubules, the interstitialinterstitial tissuetissue includes connective tissue cellsincludes connective tissue cells and fibers, vessels, and Leydig cellsand fibers, vessels, and Leydig cells – Leydig cells -Leydig cells - produceproduce testosterone.testosterone.
- 9. Imaging ModalitiesImaging Modalities UltrasoundUltrasound Modality of choiceModality of choice – 99% sensitive99% sensitive – 98% accurate at98% accurate at intratesticular vsintratesticular vs extratesticularextratesticular techniquetechnique – support scrotum onsupport scrotum on toweltowel – highest MHzhighest MHz transducer (8 or 15)transducer (8 or 15) – color and dopplercolor and doppler – Do normal side first ifDo normal side first if painpain NormalNormal – homogeneoushomogeneous – bright mediastinumbright mediastinum – TransmediastinalTransmediastinal artery or appendixartery or appendix testistestis
- 10. Imaging ModalitiesImaging Modalities MRIMRI problem solverproblem solver when US inconclusivewhen US inconclusive cryptorchidismcryptorchidism TechniqueTechnique support scrotum with warmsupport scrotum with warm towelstowels surface coil; small fovsurface coil; small fov T1W and FSET2W (SSFSE),T1W and FSET2W (SSFSE), several planesseveral planes 3mm3mm Gd?Gd? Screen abd/pelvis for nodesScreen abd/pelvis for nodes NormalNormal homogeneous, intermediatehomogeneous, intermediate on T1W and bright on T2Won T1W and bright on T2W tunica albiginea andtunica albiginea and mediastinum darkmediastinum dark
- 11. Imaging ModalitiesImaging Modalities CTCT used for staging of testicular cancer and forused for staging of testicular cancer and for inguinal hernias and infection (Fourniersinguinal hernias and infection (Fourniers gangrene)gangrene) Nuclear MedicineNuclear Medicine ?PET/CT?PET/CT
- 12. MassesMasses Key: intra vs extratesticular; solid vs cystKey: intra vs extratesticular; solid vs cyst IntratesticularIntratesticular solid - most malignant and germ cell originsolid - most malignant and germ cell origin mimics/tumor like lesions - infarcts,mimics/tumor like lesions - infarcts, orchitis/abscess and hematomaorchitis/abscess and hematoma – Orchiectomy for benign disease will occurOrchiectomy for benign disease will occur cystcyst ExtratesticularExtratesticular solid - most are benignsolid - most are benign CysticCystic CalcificationsCalcifications
- 13. Testicular CancerTesticular Cancer #1 cancer killer of young men#1 cancer killer of young men peak age 20 -45; 90% whitepeak age 20 -45; 90% white – Incidence of GCT increased inIncidence of GCT increased in cryptorchidismcryptorchidism PresentationPresentation – painless mass, mild pain or heavinesspainless mass, mild pain or heaviness – 10% present with acute scrotum10% present with acute scrotum US study of choiceUS study of choice 95% survival rate95% survival rate
- 14. Testicular CancerTesticular Cancer ClassificationClassification – Germ Cell (90%) - MalignantGerm Cell (90%) - Malignant SeminomaSeminoma Non-seminoma (embryonal cell,Non-seminoma (embryonal cell, choriocarcinoma, teratoma, yolk sac)choriocarcinoma, teratoma, yolk sac) MixedMixed – Non-Germ cell –rare; usually benignNon-Germ cell –rare; usually benign leydigleydig sertolisertoli – SecondarySecondary leukemia, lymphomaleukemia, lymphoma met (prostate)met (prostate)
- 15. Testicular Cancer - GCTTesticular Cancer - GCT SpreadSpread – LymphaticLymphatic follows veinsfollows veins 1st echelon nodes1st echelon nodes – retroperitoneal at kidneysretroperitoneal at kidneys Further tumorFurther tumor – iliac nodesiliac nodes – supraclavicularsupraclavicular epididymal & skin involvementepididymal & skin involvement lead to inguinal nodeslead to inguinal nodes – hematogeneous and directhematogeneous and direct invasion later (x chorio)invasion later (x chorio) lung>liver and brainlung>liver and brain
- 16. Testicular Cancer - GCTTesticular Cancer - GCT StagingStaging – TNMTNM – PracticalPractical low stagelow stage – testis, epi ortestis, epi or cordcord – mild nodesmild nodes Advanced stageAdvanced stage – skinskin – heavy nodesheavy nodes – hemotogeneoushemotogeneous
- 17. Testicular Cancer - GCTTesticular Cancer - GCT Tumor markersTumor markers alpha-fetoprotein, human chorionicalpha-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropingonadotropin well-established role in the diagnosis,well-established role in the diagnosis, staging,staging, prognosis, and follow-up of germ cell tumorsprognosis, and follow-up of germ cell tumors
- 18. Testicular Cancer -Testicular Cancer - ImagingImaging UltrasoundUltrasound hypoechoic masshypoechoic mass heterogeneous, echogenic, calcification,heterogeneous, echogenic, calcification, cystic, multiple or completely replace thecystic, multiple or completely replace the testistestis may show increased vascularitymay show increased vascularity Small tumors usually hypovascularSmall tumors usually hypovascular MRIMRI Isointense on T1W and hypointense on T2WIsointense on T1W and hypointense on T2W
- 19. SeminomaSeminoma Most common GCTMost common GCT slightly older ageslightly older age – does not occurdoes not occur before pubertybefore puberty uniform,uniform, hypoechoichypoechoic (hypointense), esp(hypointense), esp when smallwhen small excellent prognosisexcellent prognosis
- 20. SeminomaSeminoma 30 yo with painless30 yo with painless massmass
- 23. Embryonal carcinomaEmbryonal carcinoma In 90% of mixedIn 90% of mixed GCT, rarely inGCT, rarely in pure formpure form MoreMore aggressiveaggressive Less wellLess well defined and lessdefined and less homogeneoushomogeneous
- 24. Yolk Sac TumorYolk Sac Tumor (endodermal sinus(endodermal sinus tumor)tumor) 80% of pediatric80% of pediatric testicular tumorstesticular tumors (Most common in(Most common in children <2yo)children <2yo) occurs in mixedoccurs in mixed GCT in adultsGCT in adults Elevated Alpha-Elevated Alpha- fetoproteinfetoprotein
- 25. TeratomaTeratoma #2 tumor in kids#2 tumor in kids common in mixed GCTcommon in mixed GCT in adultsin adults tend to be benign in kidstend to be benign in kids more unpredictable inmore unpredictable in adultsadults complex, cysticcomplex, cystic appearanceappearance controversial recontroversial re epidermoid cystepidermoid cyst
- 26. ChoriocarcinomaChoriocarcinoma Rare but mostRare but most aggressive GCTaggressive GCT EarlyEarly hematogeneoushematogeneous mets commonmets common elevated HcGelevated HcG Poor prognosisPoor prognosis HeterogeneousHeterogeneous massmass
- 27. Mixed Germ Cell TumorMixed Germ Cell Tumor More common thanMore common than any other testicularany other testicular tumor excepttumor except seminomaseminoma Any combination ofAny combination of cell typescell types variety of cell typesvariety of cell types expressed inexpressed in variablevariable appearanceappearance
- 28. ““burned out” Germ Cellburned out” Germ Cell TumorTumor Phenomenon of patientPhenomenon of patient presents with widespreadpresents with widespread metastatic disease withmetastatic disease with involuted primary tumorinvoluted primary tumor ?etiology. ?outgrown blood?etiology. ?outgrown blood supplysupply Primary tumors have a variablePrimary tumors have a variable appearance. Small and can beappearance. Small and can be hypoechoic, hyperechoic, orhypoechoic, hyperechoic, or merelymerelyan area of focalan area of focal calcification.calcification. Histologic analysis may revealHistologic analysis may reveal minute amounts of residualminute amounts of residual tumor or only dense depositstumor or only dense deposits of collagenof collagen with scatteredwith scattered inflammatory cellsinflammatory cells 22 yo presented with back pain and lower extremity weakness. Initial work-up showed an extradural mass, retroperitoneal adenopathy, and lung metastases. Physical examination of the testes was negative. After biopsy of a cervical node revealed metastatic germ cell tumor, scrotal sonography was performed 22 yo presented with back pain and lower extremity weakness. Initial work-up showed an extradural mass, retroperitoneal adenopathy, and lung metastases. Physical examination of the testes was negative. After biopsy of a cervical node revealed metastatic germ cell tumor, scrotal sonography was performed
- 29. CryptorchidismCryptorchidism 6% of full term neonates; 1% at one6% of full term neonates; 1% at one year; 10% bilateralyear; 10% bilateral Increased risk of:Increased risk of: – Testicular carcinoma (most seminomas)Testicular carcinoma (most seminomas) – InfertilityInfertility Disordered embryogenesisDisordered embryogenesis Associated with other GU anomalies:Associated with other GU anomalies: agenesis/ectopy of kidney andagenesis/ectopy of kidney and absence/cyst of SVabsence/cyst of SV Risk of cancer increased in contra-lateralRisk of cancer increased in contra-lateral testis, even if descendedtestis, even if descended Risk of cancer not reduced appreciablyRisk of cancer not reduced appreciably with orchiopexywith orchiopexy – Note: single post-pubertal bxNote: single post-pubertal bx recommended to identify intratubularrecommended to identify intratubular germ cell neoplasm (cis) as marked riskgerm cell neoplasm (cis) as marked risk factorfactor
- 30. CryptorchidismCryptorchidism Clinical Problem: nonpalpableClinical Problem: nonpalpable testistestis – DDX: cryptorchidism vs agenesisDDX: cryptorchidism vs agenesis – Important distinctionImportant distinction Agenesis: no txAgenesis: no tx Cryptorchidism: orchiopexy atCryptorchidism: orchiopexy at 2yrs; close exam and bx post-2yrs; close exam and bx post- pubescentpubescent – Role of imaging:Role of imaging: MRI study of choice (US and CTMRI study of choice (US and CT lack specificity)lack specificity) – Laporoscopy: Many feel study ofLaporoscopy: Many feel study of choice (dx and tx)choice (dx and tx)
- 31. Retractile TestisRetractile Testis (Hyper)active cremasteric reflex, prompted(Hyper)active cremasteric reflex, prompted by anxiety, trauma, etc., may pull the testisby anxiety, trauma, etc., may pull the testis out of the scrotum (prescrotal orout of the scrotum (prescrotal or intracanalicular)intracanalicular) Not uncommon in trauma setting, especiallyNot uncommon in trauma setting, especially in boys (2-3%).in boys (2-3%). Recommend PE to differentiate retractileRecommend PE to differentiate retractile testis from true cryptorchidismtestis from true cryptorchidism
- 32. MicrolithiasisMicrolithiasis Uncommon (.5%)Uncommon (.5%) increased associationsincreased associations cryptorchidism,cryptorchidism, infertility, Klinefelterinfertility, Klinefelter syndrome, Downsyndrome, Down syndrome, alveolarsyndrome, alveolar microlithiasis, and,microlithiasis, and, mostmost important,important, testiculartesticular carcinomacarcinoma Calculi withinCalculi within Seminiferous tubulesSeminiferous tubules
- 33. MicrolithiasisMicrolithiasis US diagnosisUS diagnosis 5 or more5 or more calcificationcalcification may be bl andmay be bl and diffuse or focaldiffuse or focal Risk or coexistentRisk or coexistent or subsequentor subsequent carcinomacarcinoma controversialcontroversial as is need andas is need and duration of us followduration of us follow upup
- 34. Non-Germ cell tumorsNon-Germ cell tumors 5% of testicular cancer5% of testicular cancer higher in pedshigher in peds Sertoli (sex cord) and LeydigSertoli (sex cord) and Leydig (interstitial) cell(interstitial) cell Also other rare cell linesAlso other rare cell lines 90% benign90% benign Indistinguishable from GCTIndistinguishable from GCT Calcifying Sertoli Cell TumorCalcifying Sertoli Cell Tumor pediatric age grouppediatric age group multiple calcified massesmultiple calcified masses PJ and Carney syndromePJ and Carney syndrome
- 35. LymphomaLymphoma 5% of testicular tumor5% of testicular tumor #1 in over 50 y/o#1 in over 50 y/o only 1% of lymphomaonly 1% of lymphoma patientspatients May beMay be only site of diseaseonly site of disease along with other diseasealong with other disease site of recurrencesite of recurrence AppearanceAppearance Indistinguishable fromIndistinguishable from GCTGCT Multiple, bl hypoechoicMultiple, bl hypoechoic nodulesnodules
- 36. Leukemia and MetsLeukemia and Mets Common site of recurrenceCommon site of recurrence primary disease uncommon hereprimary disease uncommon here Appearance variableAppearance variable uni or bluni or bl focal or diffusefocal or diffuse hypo or hyperechoichypo or hyperechoic Solid organ metsSolid organ mets rare; usually disease widespreadrare; usually disease widespread prostate and lungprostate and lung
- 37. Tumor-like lesionsTumor-like lesions ““intratesticular mass is cancer untilintratesticular mass is cancer until proven otherwise”proven otherwise” Traditional teaching: 95% malignantTraditional teaching: 95% malignant BUT, more benign lesions being identifiedBUT, more benign lesions being identified Not all testicular lesions are tumorsNot all testicular lesions are tumors As many as 30% of orchiectomies for testicular lesionsAs many as 30% of orchiectomies for testicular lesions end up being benignend up being benign ((Haas GP, Shumaker BP, Cerny JC. The high incidence ofHaas GP, Shumaker BP, Cerny JC. The high incidence of benign testicular tumors. J Urolbenign testicular tumors. J Urol 19861986;136:1219 -1220);136:1219 -1220) recognition of these entities may prevent needlessrecognition of these entities may prevent needless orchiectomyorchiectomy Still, rather needless orchiectomy thanStill, rather needless orchiectomy than missed cancer. Thus will havemissed cancer. Thus will have orchiectomy for benign disease.orchiectomy for benign disease.
- 38. Tumor-like lesionsTumor-like lesions DDX:DDX: orchitisorchitis Hematoma/contusionHematoma/contusion infarctinfarct cyst (see next)cyst (see next) – mimics teratomamimics teratoma adrenal restsadrenal rests – 2% of adults have2% of adults have – Enlarged in CAH orEnlarged in CAH or rarely Cushingsrarely Cushings – BL hypo massesBL hypo masses sarcoidosissarcoidosis sperm extractionsperm extraction
- 39. Sperm Extraction*Sperm Extraction* Sperm extraction forSperm extraction for infertility are becominginfertility are becoming more commonmore common In a % (varies from20-In a % (varies from20- 80%) Focal testicular80%) Focal testicular lesions can resultlesions can result ?hematoma, infarct?hematoma, infarct FindingsFindings anterior andanterior and subcapsularsubcapsular hypoechoichypoechoic hyperechoic, calcifichyperechoic, calcific History may allow closeHistory may allow close F/UF/U *S Strauss, AJR 2001 176: 113
- 40. Intra-testicular CystsIntra-testicular Cysts OverviewOverview Tunica Albuginea cystsTunica Albuginea cysts Simple cystSimple cyst Cystic transformation of the rete testesCystic transformation of the rete testes epidermoidepidermoid intratesticular spermatoceleintratesticular spermatocele Intratesticular varicoceleIntratesticular varicocele AbscessAbscess InfarctInfarct
- 41. Tunica Albuginea CystTunica Albuginea Cyst ?etiology?etiology Middle ageMiddle age Key to diagnosisKey to diagnosis peripheral locationperipheral location simple cystsimple cyst usually 2-5 mmusually 2-5 mm
- 42. Simple CystSimple Cyst Usually >40 yoUsually >40 yo 2mm to 2cm2mm to 2cm single or multiplesingle or multiple Usually nearUsually near mediastinummediastinum
- 43. EpidermoidEpidermoid Keratonizing squamousKeratonizing squamous epithelium filled withepithelium filled with cheesy laminated stuffcheesy laminated stuff appearanceappearance echogenic rimechogenic rim ““onion skinned” due toonion skinned” due to layerslayers ““solid” appearingsolid” appearing avascularavascular
- 44. EpidermoidEpidermoid Unable to totallyUnable to totally exclude solid lesionexclude solid lesion usually andusually and orchiectomy oftenorchiectomy often neededneeded MRIMRI high signal on T1high signal on T1 and T2and T2
- 45. Cystic Transformation ofCystic Transformation of the Rete Testisthe Rete Testis Due to obstruction of efferentDue to obstruction of efferent ductules with resultant ectasiaductules with resultant ectasia older menolder men FindingsFindings uni or bluni or bl tubular cystic areastubular cystic areas in/near mediastinumin/near mediastinum epididymal cystsepididymal cysts DDX: cystic GCT (esp teratoma)DDX: cystic GCT (esp teratoma) usually has soft tissueusually has soft tissue not tubularnot tubular MRI can may be helpfulMRI can may be helpful
- 46. Intra-testicularIntra-testicular SpermatoceleSpermatocele Near mediastinumNear mediastinum cystic, can becystic, can be septatedseptated containscontains spermatozoaspermatozoa
- 47. Intras-testicularIntras-testicular VaricoceleVaricocele ?etiology. ??etiology. ? significancesignificance May cause painMay cause pain (+-)extratesticular(+-)extratesticular varicocelesvaricoceles FindingsFindings tubular, serpigineoustubular, serpigineous structures withstructures with venous doppler/colorvenous doppler/color flow which increasesflow which increases with valsalvawith valsalva
- 48. Testicular TorsionTesticular Torsion Most common in adolescentsMost common in adolescents Acute scrotumAcute scrotum DDXDDX – torsiontorsion – orchitisorchitis – traumatrauma – tumortumor Due to “bell and clapper”Due to “bell and clapper” deformitydeformity lackof normal fixation in thelackof normal fixation in the scrotumscrotum Urologic EmergencyUrologic Emergency salvage rate related to timesalvage rate related to time – 90%-100% detorsion within 690%-100% detorsion within 6 hours of painhours of pain – 20%-50% after 12 hours20%-50% after 12 hours – 0%-10% if detorsion greater0%-10% if detorsion greater than 24 hoursthan 24 hours consider doing own USconsider doing own US
- 49. Testicular TorsionTesticular Torsion FindingsFindings Early, testis is normal; laterEarly, testis is normal; later becomes enlarged andbecomes enlarged and hypoechoichypoechoic Lack ofLack of SignificantSignificant detectable flowdetectable flow reactive hydrocelereactive hydrocele
- 50. Torsion of AppendigesTorsion of Appendiges Torsed appendix testis
- 51. Scrotal TraumaScrotal Trauma 2 Categories2 Categories penetrating (surgery)penetrating (surgery) blunt (imaging)blunt (imaging) TesticularTesticular Fracture/ruptureFracture/rupture disruption of t. albugineadisruption of t. albuginea with bleeding andwith bleeding and extrusion of S.T.extrusion of S.T. surgical emergencysurgical emergency Trauma inducedTrauma induced torsion/Infarct a knowtorsion/Infarct a know complicationcomplication Types of injury: Contusion Hematoma Fracture/rupture hematocele Types of injury: Contusion Hematoma Fracture/rupture hematocele
- 52. Scrotal TraumaScrotal Trauma UltrasoundUltrasound Normal - excludes seriousNormal - excludes serious injuryinjury hematoma - echogenic orhematoma - echogenic or hypoechoic; roundedhypoechoic; rounded Hematocele - extratesticularHematocele - extratesticular fluid; echoes or echogenicfluid; echoes or echogenic Infarct - absent flowInfarct - absent flow FractureFracture – Heterogeneous testicle;Heterogeneous testicle; diffuse or focaldiffuse or focal – irregular or ill-defined contourirregular or ill-defined contour or bulgeor bulge – often just a “often just a “messmess””
- 53. Scrotal TraumaScrotal Trauma MRIMRI – May play future roleMay play future role in detection ofin detection of disruption of thedisruption of the tunica albuginea (ietunica albuginea (ie rupture)rupture)
- 54. Scrotal Trauma:Scrotal Trauma: extremeextreme mountain bikersmountain bikers.. Krauscher F Radiology 2001May;219(2):427-31USKrauscher F Radiology 2001May;219(2):427-31US
- 55. Inflammatory DiseaseInflammatory Disease Epididymitis/orchitisEpididymitis/orchitis usually retrotrade infection from bladder and prostateusually retrotrade infection from bladder and prostate rarely traumatic, surgical, etcrarely traumatic, surgical, etc orchitis from epididymitis (except mumps)orchitis from epididymitis (except mumps) ““acute scrotum” in adolescents (kids,acute scrotum” in adolescents (kids, elderly)elderly) testicular torsiontesticular torsion traumatrauma infectioninfection torsion of epididymal or testicular appendagestorsion of epididymal or testicular appendages Imaging is to confirm diagnosis andImaging is to confirm diagnosis and excluded complication (surgery)excluded complication (surgery) abscessabscess infarctioninfarction
- 56. Inflammatory DiseaseInflammatory Disease Ultrasound FindingsUltrasound Findings – involves epididymisinvolves epididymis plus/minus testisplus/minus testis focal or diffusefocal or diffuse enlargementenlargement hypoechogenicityhypoechogenicity INCREASED FLOWINCREASED FLOW reactive hydrocelereactive hydrocele Nuclear medicineNuclear medicine increased flow andincreased flow and activityactivity
- 57. Inflammatory DiseaseInflammatory Disease MRIMRI edema andedema and inflammation oninflammation on T2WT2W increasedincreased enhancementenhancement
- 58. Orchitis with InfarctionOrchitis with Infarction 58 yo with scrotal58 yo with scrotal pain and swellingpain and swelling for 4 daysfor 4 days
- 59. ExtratesticularExtratesticular PathologyPathology Normal Extratesticular VariantsNormal Extratesticular Variants Spermatocele and epididymal cystSpermatocele and epididymal cyst Sperm granulomaSperm granuloma VaricoceleVaricocele HydroceleHydrocele HerniaHernia Extratesticular TumorExtratesticular Tumor
- 60. Extratesticular VariantsExtratesticular Variants Appendix of theAppendix of the epididymisepididymis Isoechoic to epididymisIsoechoic to epididymis May calcifyMay calcify Appendix of the testesAppendix of the testes Isoechoic to testesIsoechoic to testes Cyst of MorgagniCyst of Morgagni Dilation of theDilation of the paradidymisparadidymis Cystic; can appearCystic; can appear solidsolid
- 61. Spermatocele andSpermatocele and epididymal cystepididymal cyst very commonvery common usually within/near head ofusually within/near head of epididymisepididymis usually asymptomatic andusually asymptomatic and present incidently or aspresent incidently or as palpable masspalpable mass Epididymal CystEpididymal Cyst Cystic on USCystic on US SpermatoceleSpermatocele UltrasoundUltrasound – Cystic (may not be ableCystic (may not be able to differentiate fromto differentiate from epididymal cyst)epididymal cyst) – Low level echoesLow level echoes – Rarely hyperechoicRarely hyperechoic
- 62. Sperm GranulomaSperm Granuloma Sperm extravasationSperm extravasation can result in granulomacan result in granuloma formationformation Often occurs afterOften occurs after vasectomyvasectomy Painful (unlike tumor)Painful (unlike tumor) UltrasoundUltrasound Isoechoic toIsoechoic to hyperechoic mass inhyperechoic mass in the epididymisthe epididymis Rarely may calcifyRarely may calcify
- 63. VaricoceleVaricocele Dilated intrascrotal veinsDilated intrascrotal veins incompetent valvesincompetent valves in testicular veinsin testicular veins rarely due to mass,rarely due to mass, etcetc Worry about unilateralWorry about unilateral right sided varicoceleright sided varicocele Infertility, heavinessInfertility, heaviness Common (15-20%)Common (15-20%) FindingsFindings L>R, bl commonL>R, bl common veins > 2-3mmveins > 2-3mm dilation excacerbateddilation excacerbated by valsalva andby valsalva and standingstanding
- 64. Hydrocele (hematoceleHydrocele (hematocele & pyocele& pyocele Fluid w/I tunica vaginalisFluid w/I tunica vaginalis HydroceleHydrocele – Small amount of fluid normalSmall amount of fluid normal – EtiologiesEtiologies congenital - persistent peritonealcongenital - persistent peritoneal communicationcommunication AcquiredAcquired – Reactive(trauma, infection, torsion)Reactive(trauma, infection, torsion) – In adults, not uncommon withIn adults, not uncommon with unknown etiology (diminishedunknown etiology (diminished reabsorbtion)reabsorbtion) HematoceleHematocele – Echogenic fluid; trauma, tumor orEchogenic fluid; trauma, tumor or surgerysurgery PyocelePyocele – Echogenic collection; septations andEchogenic collection; septations and debrisdebris
- 65. HerniaHernia Via patentVia patent processus vaginalisprocessus vaginalis complex masscomplex mass look for peristalsislook for peristalsis
- 66. Extratesticular tumorExtratesticular tumor Rare, mostly benignRare, mostly benign Adenomatoid tumorAdenomatoid tumor Only tumor with anyOnly tumor with any frequencyfrequency HamartomatousHamartomatous lesionlesion Adolescents andAdolescents and young adultsyoung adults Tail of epididymisTail of epididymis most common sitemost common site Isoechoic toIsoechoic to hyperechoichyperechoic
- 67. ReviewReview Solid massSolid mass – GCTGCT SeminomaSeminoma Non-seminomaNon-seminoma – Embryonal, yolk sac, teratoma, choriocarcinoma, mixedEmbryonal, yolk sac, teratoma, choriocarcinoma, mixed – Sertoli; LeydigSertoli; Leydig – Secondary (Lymphoma, mets)Secondary (Lymphoma, mets) – MimicsMimics Orchitis, trauma, infarct, adrenal, sarcoid, sperm extractionOrchitis, trauma, infarct, adrenal, sarcoid, sperm extraction – Cystic lesionsCystic lesions EpidermoidEpidermoid Cystic lesionsCystic lesions Tunica Albuginea cystsTunica Albuginea cysts Simple cystSimple cyst Cystic transformation of the rete testesCystic transformation of the rete testes epidermoidepidermoid intratesticular spermatoceleintratesticular spermatocele Intratesticular varicoceleIntratesticular varicocele AbscessAbscess InfarctInfarct TorsionTorsion TraumaTrauma EpidimoorchitisEpidimoorchitis Extratesticular DiseaseExtratesticular Disease – Normal Extratesticular VariantsNormal Extratesticular Variants – Spermatocele and epididymal cystSpermatocele and epididymal cyst – Sperm granulomaSperm granuloma – VaricoceleVaricocele – HydroceleHydrocele – HerniaHernia – Extratesticular TumorExtratesticular Tumor Adenomatoid tumorAdenomatoid tumor
Hinweis der Redaktion
- Seminoma in an Undescended Testis -- Woodward 231 (2): 388 -- Radiology (Radiology 2004;231:388-392.) Diagnosis Please A 47-year-old man presented with a 1-month history of progressive abdominal pain. He was in good health until this time, and he had not previously undergone surgery. A right lower-quadrant mass was noted at physical examination. A computed tomographic (CT) examination was performed. Figure a. Transverse CT scans obtained after administration of intravenous and oral contrast material. (a) CT scan obtained through the level of the kidneys shows bowel within the right renal fossa (arrow) because the right kidney is absent. Note the small amount of free fluid. (b, c) Large right-sided soft-tissue attenuation mass with some areas of peripheral enhancement superiorly (white arrow in b) and necrosis inferiorly (white arrow in c). Note compressed inferior vena cava (black arrow). (d) CT scan obtained through the bladder base shows a normal left seminal vesicle (arrow) with absence of the right seminal vesicle. (e) Absent right spermatic cord and normal left spermatic cord (arrow). the right spermatic cord is absent, which indicates either incomplete descent or agenesis of the right testis. The differential diagnoses for a retroperitoneal mass are many and include both benign and malignant entities. Benign lesions include retroperitoneal fibrosis, which on occasion can make bulky masses, and extramedullary hematopoiesis. The large size and focal nature of this mass makes these diagnoses unlikely. Lymphoma and metastatic adenopathy are two of the most common soft-tissue masses seen in the retroperitoneum and should be considered. In addition, primary tumors of either neurogenic or mesenchymal origin should be included in the differential diagnoses. These tumors most commonly include paraganglioma (patients are usually symptomatic), liposarcoma (visible fat may not be depicted with CT in aggressive high-grade tumors), leiomyosarcoma, and malignant fibrous histiocytoma. There is a great deal of overlap in the imaging findings of many of these masses. None of the above diagnoses would account for the other findings, which include absence of the right spermatic cord, kidney, and seminal vesicle. One potential explanation would be a tumor within an ectopic kidney associated with agenesis of the right seminal vesicle and testis. None of the images, however, show normal renal parenchyma. Even with a very large or infiltrating renal tumor, some normal parenchyma can usually be identified. Given the lack of any identifiable kidney on the right side, it is more likely congenitally absent than ectopic. The findings of an absent right spermatic cord, kidney, and seminal vesicle—in combination with the soft-tissue mass located along the path of testicular descent—make the most likely diagnosis tumor within an undescended testis. Cryptorchidism results from the abnormal formation and descent of the testes. The testes form from genital ridges, which lie on both sides of the midline and extend from T6 through S2 vertebrae in the developing embryo. Between the 7th and 12th weeks of gestation, the testes contract and become more ovoid as they begin their descent into the pelvis. They remain near the deep inguinal ring until the 7th month of gestation, when they begin their descent through the inguinal canal into twin scrotal sacs. Passage through the inguinal canal is aided by both the processus vaginalis and the shortening of the gubernaculum. The processus vaginalis is a sock-like evagination of peritoneum that elongates caudally through the abdominal wall into the scrotum and creates a path for the descending testis. The gubernaculum is a ligamentous cord that extends from the testis to the scrotum. The testes remain retroperitoneal throughout their descent but are intimately associated with the posterior wall of the processus vaginalis (1,2). At approximately 8 weeks gestational age, the Leydig cells begin to secrete testosterone, thus inducing this process. In addition, because of this hormonal influence, the mesonephric (wolffian) ducts differentiate into the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and ejaculatory ducts. Concurrently, the Sertoli cells secrete müllerian inhibiting factor, which results in regression of the paramesonephric (müllerian) ducts. A vestigial remnant of this system may persist as the appendix testis (1,2). Cryptorchidism is present in approximately 6% of full-term neonates and approximately 0.8% of infants at 1 year of age. It can be bilateral in 10% of patients (3,4). Because of its association with other urinary tract abnormalities, cryptorchidism is thought to be one manifestation of a generalized defect in genitourinary embryogenesis. Other associated malformations include renal agenesis or ectopias, ureteral duplications, seminal vesicle agenesis or cysts, and hypospadias (5–9). Cryptorchidism is also associated with infertility and is a well-recognized risk factor for testicular carcinoma. Approximately 90% of these tumors are seminomas, especially those that occur in the abdominally located testis. Although the overall incidence of cryptorchidism is low (<1%), a history of an undescended testis is present in 3.5%–14.5% of patients with testicular tumors (9). The pathophysiology of malignant transformation in these testes is not completely understood. One hypothesis is that cryptorchidism is not merely incomplete descent of the testis, but that it reflects a generalized defect in embryogenesis and results in bilateral dysgenetic gonads. An embryologic defect in testicular formation is supported by several important clinical observations. The most compelling of these is that risk for testicular carcinoma is not limited to the undescended testis but extends to the contralateral testis, even if it is normally descended. Thus, the increased risk of carcinoma cannot be attributed to local environmental factors, such as increased temperature in the abdomen versus the scrotum. While it is true that the risk of carcinoma increases with the degree of ectopy (intraabdominal testes are at greater risk than those in the inguinal canal), this also supports the theory if it is assumed that the greatest degree of ectopy reflects the greatest perturbation of embryogenesis. The defective embryogenesis hypothesis is further supported by the observation that orchiopexy, even at an early age, does not appreciably decrease the risk of developing a tumor (9). The majority of cryptorchid testes lie distal to the external inguinal ring and are palpable. Nonpalpable testes are most commonly located within the inguinal canal, but they can be located anywhere along the path of descent from the abdomen. Testicular agenesis has been reported to be present in 15%–63% of patients with a nonpalpable testis (4,10). The distinction between agenesis and maldescent is critical, as orchiopexy should be performed in all patients with undescended testes. This is usually performed between 1 and 2 years of age. If performed later, the testis will have undergone marked morphologic change, with fibrosis and collagen deposition adversely affecting spermatogenesis and fertility (11). While orchiopexy improves fertility, it does not alter the risk of developing a carcinoma. Because of this increased risk, testicular biopsies have been recommended to aid in the identification of intratubular germ cell neoplasia of the unclassified type (carcinoma in situ). If the biopsy results are positive for intratubular neoplasia, the patient has a 50% chance of developing invasive carcinoma; however, if the biopsy results are negative for intratubular neoplasia, the patient does not have an increased risk for developing carcinoma. A single postpubertal biopsy of each testis at 18–20 years of age is suggested and appears to be adequate for identification of high-risk patients (9,12). Imaging can be helpful in localizing a nonpalpable testis. An undescended testis will appear hypoechoic with ultrasonography (US), and a mediastinum testis should be identified for confident diagnosis. There are many potential pitfalls, including possible confusion with lymph nodes and the pars infravaginalis gubernaculi, which is a bulbous termination of the gubernaculum (4,13). More importantly, agenesis cannot be discriminated from atrophy with US (3,4). CT also lacks the specificity and sensitivity that are needed to diagnose agenesis. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging has the advantage of improved soft-tissue contrast, but reports have varied as to its usefulness (11,14). The results of a study by Lam et al (15) showed that gadolinium-enhanced MR venography performed in conjunction with routine pelvic MR imaging increased sensitivity for differentiation of agenesis from ectopia. Because surgery is obviated only if the testis can be proved to be absent, many urologists feel that the treatment of choice is laparoscopy, which can be both diagnostic and therapeutic (16,17). Some cases, however, will still require open inguinal exploration and abdominal laporotomy (18). Preoperative imaging may help in surgical planning in these patients.
- Upper image is venogram