A Tour In Egypt
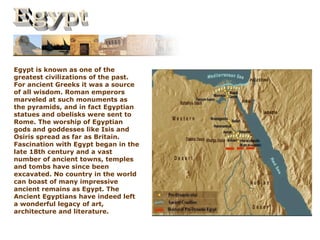
- 1. Egypt is known as one of the greatest civilizations of the past. For ancient Greeks it was a source of all wisdom. Roman emperors marveled at such monuments as the pyramids, and in fact Egyptian statues and obelisks were sent to Rome. The worship of Egyptian gods and goddesses like Isis and Osiris spread as far as Britain. Fascination with Egypt began in the late 18th century and a vast number of ancient towns, temples and tombs have since been excavated. No country in the world can boast of many impressive ancient remains as Egypt. The Ancient Egyptians have indeed left a wonderful legacy of art, architecture and literature.
- 2. The Nile River is possibly the most famous river in history. It was by its banks that one of the oldest civilizations in the world began. Not surprisingly, the Nile teems with life. Many different types of animals, birds, and fish all call the Nile River home. Hundreds of years ago, even hippos and lions could be found here in the Nile Valley. Length: (From White Nile Source to Mouth) 6695km (4184 miles). Sources: The White Nile: Lake Victoria, Uganda. The Blue Nile: Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Cities: The major cities that are located on the edge of the Nile and White Nile are: Cairo, Gondokoro, Khartoum, Aswan, Thebes/Luxor, Karnak, and the town of Alexandria lies near the Rozeta branch.
- 3. Egypt was a cradle of civilization that allowed the same basic language and culture to flourish for nearly 3,000 years. For most of this long history, Pharaoh was 'Lord of the Two Lands' - the Nile valley and the broad Delta. Each major pyramid was a tomb for a king of Egypt. The pyramid complex was an economic engine too - employing people and redistributing wealth. Thus the pyramids were a major catalyst in the development of Egypt as one of the world's first true state. The livestock and produce from these estates was then passed on to the workforce and to the priests and special classes of people who served the pyramid complex. With the building of the pyramids, new farms, ranches and whole new towns were founded in the provinces. The pyramids of Giza were built over the span of three generations - by Khufu, his second reigning son Khafre, and Menkaure. At Giza the pyramid reached its climax and the standard features of the Old Kingdom pyramid complex - the mortuary and valley temple - were expanded and formalized.
- 4. The Great Pyramid of Khufu was called Akhet Khufu 'The Horizon of Khufu'. It contains about 2,300,000 blocks of stone, each of which is thought to weigh on average 2.5 tons. Its base is 230.33m long, and it rose to a height of 146.59m. The finished pyramid was surrounded by a Turah limestone wall, over 8m high, enclosing a court which was paved in limestone. Access to this court could only be gained via the valley temple, causeway and mortuary temple. Khufu's pyramid has 3 Queen's pyramids built at the front of the pyramid The 1st pyramid is thought to have been built for Queen Hetepheres, who was the wife of Sneferu and probably the mother of Khufu. Texts in her burial chamber referred to her as 'Daughter of the God' and 'Mother of the King'. The 2nd pyramid might belong to Queen Meritetes who lived through the reigns of Sneferu, Khufu and and Khafre. The 3rd pyramid, which is thought to have belonged to Queen Henutsen, is the only one of the three Queen's pyramids which still has its mortuary chapel still intact.
- 5. Khafre's pyramid, called 'Khafre is Great', rose from a 705-foot wide base to a height of 471 feet at an angle of 53 ؛7 '. It has two entrances, each opening onto a descending passage that leads to a chamber. The smallest of the Giza Pyramids is that of Menkaure. The pharoah, who ruled for at least 26 years, died before his furerary complex was completed, and parts of it were finished by his son Shepseskaf. Many additions were made to the complex during the Fifth and Sixth dynasties, indicating that, despite his untimely death, the king's cult flourished for more than three centuries. Originally about 240 feet high, the pyramid now measures 204 feet on a base of 357 feet wide.
- 6. The Sphinx on the other hand, stands alone, with no rivals either on site or elsewhere among all the sphinxes of Egypt. Truly, this is the Great Sphinx, as well as very likely being the first of the breed. The Great Sphinx started off as a knoll of rock at the bottom of the Giza Plateau towards the valley of the Nile. The Sphinx is carved out of the living rock, though parts of it have been repaired with blocks of stone. The head is made of hard limestone of the same sort as was quarried around the pyramids. The body on the other hand, is made of poorly consolidated and therefore readily eroded limestone. The rock improves again at the base of the monument, with a return to harder reef-formed limestone that has allowed some carved details of the beast to remain visible after at least four-and- a-half thousand years of natural and human attrition. The monument was made from the start to point directly to sunrise. The Great Sphinx is huge. The length of the body is more than 74 m; its height from the floor of the enclosure to the top of the head some 20 m. The extreme width of the face reaches over 4 m, the mouth being 2 m wide; the nose would have been more than 1.5 m.
- 7. The Step Pyramid Complex of Djoser (also spelled Zozer) was built during the Third Dynasty (ca. 2800 B.C.) in what is now Saqqara, Egypt. Djoser's Step Pyramid is generally considered the first tomb in Egypt to be built entirely of stone Saqqara was one of the main burial fields of the ancient city of Memphis, capital of Ancient Egypt during the Old Kingdom. It is located some 40 kilometers from Egypt’s modern day capital, Cairo. On a clear day, its most prominent monument, the Step Pyramid of Djoser, can be seen from Giza, which lies some 17 kilometers to the North, and from Dashur, which lies 10 kilometers to the South.
- 8. Two rectangular boat pits found on the south side of the Great Pyramid were discovered in 1954, covered by huge limestone slabs, containing the dismantled remains of two Royal Boats. It is thought that these boats transported Khufu's body to his pyramid
- 9. Luxor is unique among the cities of the world. Wherever you tread, you feel you are experiencing the past and the present at one and the same time. There is hardly a place in the city that does not have a relic that tells of the grandeur of the Ancient Egyptians several thousand years ago. Luxor Temple built by the two pharaohs: Amenhotep III and Ramses II. The temple was dedicated to Amun-Ra, whose marriage to Mut was celebrated annually, when the sacred procession moved by boat from Karnak to Luxor Temple.
- 10. This is the greatest place of worship in history. It includes many singular temples, dedicated to Amun, his wife (Mut), and their son (Khonsu), the moon deity. Since the Arab conquest, it became known as “Al-Karnak" (The fort). The temple starts with the avenue of the Rams, representing Amun: symbol of fertility and growth. Beneath the rams' heads , small statues of Ramses II were carved.
- 11. These are the two tombs, ordered by the kings and queens of the New Kingdom to be carved in the rock-faces of the valley so as to safeguard them against grave- robbers. The tomb is composed of several rooms and corridors leading to the Burial Chamber. The most important of these tombs are those of Tut-Ankh- Amun, Ramses III, Seti I, Ramses VI, Amenhotep II, Hur-Moheb and Tuthmosis III. The chief tombs of the Valley of the Queens are those of Queen Nefertiti (Wife of ramses II).
- 12. This temple was built by Queen Hatshepsut to perform the ritesof the nether world. Deir el-Bahari is a fairly recent nomenclature from the 7th century B.C. when the Copts used it as a monastery. The temple is composed of three impressive rising terraces, split by a road.
- 13. Abu Simbel is a temple built by Ramesses II (c.1279-1213 B.C.E.) in ancient Nubia, where he wished to demonstrate his power and his divine nature. Four colossal (65 feet/20 meters high) statues of him sit in pairs flanking the entrance. The head and torso of the statue to the left of the entrance fell during ancient times, probably the result of an earthquake. This temple faces the east, and Re- Horakhty, one manifestation of the sun god, is shown inside the niche directly above the entrance. The alignment of the temple is such that twice a year the sun’s rays reach into the innermost sanctuary to illuminate the seated statues of Ptah, Amun-Re, Ramesses II, and Re- Horakhty.
- 14. The Temple of Hathor at Abu Simbel was built by Ramesses II (c.1279-1213 B.C.E.) to honor both Hathor as the goddess of love/music and his wife Nefertari as the deified queen. The facade, resembling a pylon, has six standing colossal (over 33 feet/10 meters high) statues. On each side of the entrance, two statues of Ramesses flank one of Nefertari dressed as Hathor. The colossal statues are, in turn, flanked by smaller statues of their children.
- 15. Between Aswan and Luxor is located the major Ptolemaic temple of Edfu - the best preserved major temple in Egypt. The temple is dedicated to the falcon god Horus and was built over a 180-year period from 237 BC to 57 BC.
- 16. On a small island in the Nile near Aswan stands the amazing Temple of Isis at Philae. This monument is possibly best known for the international effort which moved it in it's entirety to the island when it's original location was threatened by the change in water level caused by the High Dam.
- 17. Golden Mummy Mask of King Tutankhamun. The Egyptian museum in Cairo was established by the Egyptian government in 1835. The present museum building was build in 1900, in the neo- classical style by the French architect Marcel Dourgnon. The museum exhibited collections now exceed 120000 objects ranges from pre historic era to the Greco-Roman period. Museum
- 18. Some pictures of what you can seeSome pictures of what you can see at the Egyptian Museumat the Egyptian Museum Alabaster Canopic Jar of Tutankhamun Beautiful Falcon Mummy Mask Princess Nofert HatshepsutOrnate mummy mask bust of Nefertiti Face of Royalty
- 19. Over180 meters high , it is the most outstanding attraction of modern Cairo. The first of the top two levels has a rotating restaurant and cafeteria. Visitors can enjoy a panoramic view of Cairo from the observation platform. Cairo
- 20. Salah ad-Din built the Citadel in 1183 A. D. as the center of government, while simultaneously extending and restoring the city fortifications, with the aim to dominate Cairo from Mokattam Hills. This huge project was incomplete at his death, and much work continued in later times. Cairo is the best preserved of all Islamic cities, and substantial parts of Salah el-Din's structures remain today. In spite of the impounding of the defensive towers, the Cairo Citadel is, from a military point of view, slightly less substantial than the Citadel of Aleppo (In syria), but it remains one of the most notable existing examples of Muslim military architecture. The skilful masonry work, and the impressive vaulting in particular have no precedent in Egypt.
- 23. in Sinai
- 24. in Sinai
- 25. In ancient Egypt the city and Library of Alexandria was the meeting place where philosophical, spiritual, and cosmological teachings flowed together to create vital new syntheses and a flourishing cultural environment.
- 26. Memorial of the unknown soldier, Alexandrian This castle was build at the original place of the miracolous Lighthouse of Alexandria, one of the seven ancient wonders. Alexandrian Library Stanly Bridge
- 27. The simplicity of sun, sea and sand. The luxury of five-star hotels, water sports, shopping and entertainment. This is Sharm el-Sheikh, one of the most accessible and developed tourist resort communities on the Sinai peninsula. All around are Bedouins, colorful tents, mountains and sea. There are small, intimate hotels with modern designs, as well as larger hotel complexes belonging to International chains, plus about all the amenities one could expect of a tourist center, including casinos, discos and nightclubs, golf courses and health facilities. In fact, with diving and snorkeling, windsurfing and other water sports, horses and camel riding, desert safaris, and great nearby antiquities attractions, it is almost impossible for a visitor to ever suffer from boredom.
- 28. In Neama Bay, Sharm El Sheikh Neama Beach is one of the center of the tourist activities. Located just north of Sharm, this area is developing into a resort town of its own. Most hotels at Neama Bay have their own, private beaches with comfortable amenities such as chairs, shades and even bars.
- 29. Some of the great treasures located under the Red Sea
- 37. Best Regards, Designed by,Mariana Samir Operations Secretary, Kodak (Egypt)