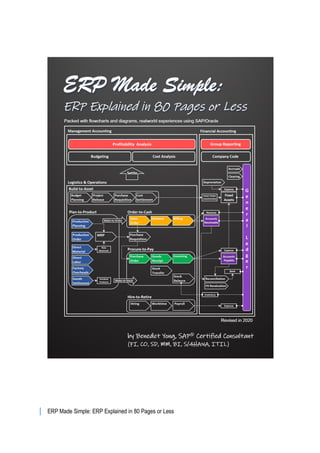
ERP Made Simple (preview)
- 1. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less
- 2. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Table of Contents Preface 1 Introduction 1.1 ERP Introduction 1.2 How does an ERP journey begin? 1.3 How does the ERP operation work? 2 Business & Processes 2.1 ERP Operations Introduction 2.2 SAP Operations Introduction 2.3 The SD Module Sales Order Structure The Sales & Distribution Process (Order-to-Cash) SD Enterprise Integration (Advanced Topics) 2.4 The MM Module Material Management Overview Centralized / Decentralized Procurement Purchase Order Structure The Procurement Process (Procure-to-Pay) MM Enterprise Integration (Advanced Topics) 2.5 The PP Module Production Planning Overview The Production Process (Plan-to-Product) Production Order Structure The Production Execution Process PP Enterprise Integration (Advanced Topics) 2.6 The PS Module Project System Overview Project System Structure The Project System Process (Engineer-to-Order) The Project System Process (Build-to-Asset) The Project System Process (Enterprise Asset) PS Enterprise Integration (Advanced Topics) 2.7 The FI Module Finance Overview Finance Structure The Finance Reporting Process (Record-to-Report)
- 3. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less The 10+1 Basic Finance Processes The Cash Management Solution FI Enterprise Integration (Advanced Topics) 2.8 The CO Module Controlling Overview Controlling Solution The Controlling Process Controlling Process: CO-PC Controlling Process: CO-PA The Budgeting Solution CO Enterprise Integration (Advanced Topics) 2.9 The HR Module Human Resource Overview Human Resource Structure The Human Resource Process (Hire-to-Retire) The 5 Basic HR Sub-modules HR Enterprise Integration (Advanced Topics) 2.10 Enterprise Architecture 2.11 Configuration Concept (Advanced Topic) 2.12 Customization Concept (Advanced Topic) 3 The ERP Career 3.1 ERP Implementation Role 3.2 ERP Support Role 3.3 The Next Frontier Appendix: SAP Mindmaps FI Mindmap CO Mindmap SD Mindmap MM Mindmap PP Mindmap PS Mindmap HR Mindmap
- 4. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Introduction ERP Introduction A software is no longer a software if we are talking about an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). An ERP is much more than a piece of software; it embodies the enterprise, its processes, its people and its culture. An ERP is cannot be used right out of the box, it has to be configured with deep considerations of the enterprise structures and goals. All these are the results of lengthy business discussions. Once an ERP strategy is made, there will be changes to the enterprise operations, in turn affects the daily lives of people using the system. An ERP program in an organization is both a threat and opportunity; it really depends on how the organization and each individual manage it. Formally, ERP belongs to a class of business systems that brings together enterprise information, primarily financial, logistical and human resource related, in order to support of enterprise level reporting planning and operations. ERP are typically modular in nature, as it plays a central role of integrating major business lines, such as sales, purchasing, manufacturing, finance, etc. The benefits of ERP are well-documented by Shang & Seddon’s ERP Benefits Framework (2002); the list includes reduced cost, reduced cycle time, improved decision-making, improved customer services, improved external/internal collaboration, empowered employee, learning facilitation, better morale. Having a centralized ERP presupposes that processes and data are consistently defined. The challenge of ERP is not in the system application itself but rather on the level of clarity the organization has of its own business processes. ERP implementation can fail either due to the organizations having conflicting processes that no ERP application can support, or the ERP itself is not flexible to handle the complex business operations – it is often more of the former than the latter.
- 5. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less In the ERP market, there are heavyweight and lightweight players. The top 3 heavyweights include SAP®, Oracle® and Microsoft®. We can use the below research by Panorama Consulting Solutions as a reference to have a feel on the industry. (Source - http://www.businessnsoftware.com/erp-market-share/, referencing Panorama Consulting Solutions, 2012) SAP provides has two primary ERP products, namely: the heavyweight SAP ECC (SAP ERP Central Component), and a lighter-weight SAP B1 (Business One). Oracle has at least 5 ERP solutions, namely: EBS (eBusiness Suite), Siebel, PeopleSoft, JD Edwards and NetSuite. Microsoft has one primary ERP product, MS Dynamics AX (aka MS Dynamics 365F&O). Following the Big 3 is Infor; it has acquired 40 softwares (of which a significant number are business systems & ERP) since its 2002 founding. There are too many Infor ERP to be listed. SAP will be used as the referenced ERP when we are in specific discussions, whilst Oracle will be used as a supplementary comparison where possible.
- 6. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less High-level diagram of the SAP ERP solution with extensions SAP ECC has very comprehensive modules to cater for enterprise needs. For logistics, it has Sales and Distribution (SD), Material Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), Quality Management (QM), Project Systems (PS), Plant Maintenance (PM). For finance, it has Financial Accounting (FI), Management Accounting (CO). For human resource, it has submodules like Personnel Administration, Benefits Administration, Payroll, and Performance Management. In addition, extension modules provide functionalities such TM (Transport Management), WM (Warehouse Management), Treasury (TRM), and Financial Supply Chain (FSCM).
- 7. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Apart from the ECC Core, SAP also provides ‘new dimension’ applications (which require extra licenses). To name a few: SAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management), SRM (Supplier Relationship Management), SCM (Supply Chain Management), BI (Business Intelligence/Data- warehouse), BPC (Business Planning & Consolidation). SRM, SCM, BI, BPC functionalities are gradually incorporated into the newer SAP HANA solution. Over the years SAP also bought over new companies and products, this further augment its capabilities to deliver. For example, SAP Hybris is positioned as Sales/Marketing cloud solution, SAP Ariba is an alternative procurement solution, and SF (SuccessFactors®) to cater for HR requirements. With the advancement of technology, in-memory technologies also made its way to ERP. Specific to SAP, the in-memory database is known as HANA® database (technical details at SAP website). HANA is a high performing native database created and used by SAP®; it allows SAP ERP applications to push application level processing into the database level - yielding even better performance and integration. S/4 HANA (aka SAP Business Suite for SAP HANA) the next generation of ERP is made possible with HANA. S/4 HANA can be deployed in the cloud or installed on-premises. The primary advantages of cloud solution are having the infrastructure support taken care by the cloud provider and the solution can be scaled for optimal usage. There are various cloud options, offering various degrees of customizations. The more interesting part of all these is, the third option – hybrid deployment. For instance, if the organization is deep into customizing its logistical modules but generic in its human resource processes, they can opt for on-premises logistics and cloud human resource. Another example will be individual on-premises subsidiaries’ ERP (SAP or non-SAP) linking back to the HQ Central Finance cloud solution. The ERP trend now is with in-memory and cloud computing. SAP, Oracle and other major ERP suppliers are supporting this vision with various offerings. We are not quite done yet before having some comparisons with Oracle - the other big player in the ERP space.
- 8. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less High-level diagram for Oracle side (for comparison purposes)
- 9. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Oracle has a different market strategy for the ERP market, it basically uses a mixed approach of building internally and buying externally. It is currently having 5 primary ERP suites, namely: E- Business Suite (EBS), Siebel, PeopleSoft, JD Edwards, and NetSuite. The Oracle support strategy for its ERP offerings is termed as ‘Oracle Applications Unlimited’. This is to say the firm is committed to support all the acquired product suites with new developments till at least 2030. Of the 5 Oracle ERP discussed, only EBS is internally built. Looking into EBS, it covers common ERP areas and more; this includes Oracle Financials, Oracle HRMS, Oracle SCM, Oracle Procurement, Oracle CRM, and Oracle Projects. Likewise for Oracle PeopleSoft and JD Edwards suites. The question remains: will there be an ultimate consolidation of these big 5, or a totally new slick ERP will arise after 2030? In spite, there is a 6th internally built Oracle ERP known as Oracle Fusion. The difference between the two ERP vendors (SAP, Oracle) is at both the marketing level and product level. In Oracle, there is a large basket of matured ERP products, giving different varieties to the customers. In SAP, attention is channeled into refining a smaller basket of ERP products (i.e. ECC and B1), while having more capacity to take-on deeper extended functionalities. All in all, the specific operating of each ERP products may differ but they are serving a common market that has common requirements. In this sense, it is more important to know what are the business requirements, rather than the exact steps to execute an operation.
- 10. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Unit Glossary for SAP Products, with industry narratives. This is needed for subsequent chapters referencing. (This is also a useful job/learning aid for those using SAP) Term Description Details SAP ECC ERP Central Component SAP on-premises Enterprise Resource Planning solution. As with most leading ERP, it is modular in nature, comprising of finance, logistics and human resource modules and submodules. The next class of SAP ERP is S/4 HANA Enterprise Management, this is an in-memory solution, with cloud options. SAP SD Sales and Distribution ECC Module. Dealing with sales orders and its distribution. SAP MM Material Management ECC Module. Dealing with external procurement and managing of inventory. SAP PP Production Planning ECC Module. Dealing with manufacturing related tasks. SAP QM Quality Management ECC Module. Dealing with quality management and inspections. Typically required when SAP PP module is used. SAP TM Transport Management ECC Module. Dealing with advanced transport planning activities. SAP WM Warehouse Management ECC Module. Dealing with warehousing planning activities. SAP PS Project Systems ECC Module. Dealing with projects. It has both logistics and controlling components; and can be applied flexibly among the two. SAP PM Plant Maintenance ECC Module. Dealing with maintenance of the physical assets (i.e. PPE - Property, Plant & Equipment). It is primarily a logistic module but has a controlling component to it. SAP SM / CS Service Management / Customer Service It refers to the used of SD and PM module, for maintenance service sales to external customers. This is prevalent for the repair/refurbishment business. SAP FI Financial Accounting ECC Module. Dealing with external regulatory reporting. FI is further broken down into AP (Accounts Payable), AR (Accounts Receivable), AA (Asset Accounting) and Bank accounting. SAP CO Management Accounting ECC Module. Dealing with internal management reporting. It is a very dynamic business function; it really depends on the organization, what it wants to do. There are 3 key areas of focus (typically): Cost Analysis,
- 11. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Budgeting, and Profitability. SAP has 3 submodules, namely: CO-OM (Overhead Management), CO-PA (Profitability Analysis) and CO-PC (Product Costing) SAP COOM Overhead Management It is a sub-module coming under CO. It caters for overheads accounting and cost allocation, using primarily Cost Centers (CC) and Internal Orders (IO) are used as Cost Objects. SAP COPA Profitability Analysis It is a sub-module coming under CO. It acts as a strategic & financial reporting tool for analyzing the profitability based on different market segments (e.g. customer, products, region, etcs). There two primary type: Account Based and Costing Based. In S/4 HANA Enterprise Management, there is new corresponding component (Account Based) known as Margin Analysis. Costing Based remains unchanged. SAP COPC Product Costing It is a sub-module coming under CO. It enables materials costs planning (cost estimates) assess cost components such as direct materials, direct labor and overheads. SAP ML Material Ledger SAP Material Ledger is a component of the Product Costing. It provides clarity on price history and difference. Based on that it can incorporate the price difference back into the material inventory. SAP CM Cash (& Liquidity) Management ECC Module. Dealing with cash position, liquidity forecast and bank management. SAP TRM Treasury (& Risk) Management ECC Module. Dealing with cash and financial assets (e.g. securities, debts, derivatives, commodities, loans) optimization, and its related risks. SAP FSCM Financial Supply Chain Management ECC Module. Dealing with optimization of Accounts Receivable (and Accounts Payable, also other cash- related) processes. SAP IM Investment Management ECC Module. Dealing with capital investment. Typically used with Asset Accounting and Project System. SAP HR Human Resource ECC Module. Dealing with human resource and human capital management. SAP CATS Cross-Application Timesheet ECC Component. Dealing with worktime tracking. It is used by various modules for cost controlling and is integrated with HR time management. SAP CRM Customer Relationship Management It is an extended application to handle the pre-sales related activities. SAP SRM Supplier Relationship Management It is an extended application to handle supplier integration and collaboration activities.
- 12. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less SAP SCM Supply Chain Management It is an extended application to handle advanced supply chain activities, such as forecasting, planning and scheduling. SAP SOP Sales & Operations Planning ECC Component. It is a flexible forecasting and planning tool with which sales, production, and other supply chain targets can be set on the basis of historical, existing, and estimated future data. In S/4 HANA Enterprise Management, there is new corresponding component known as Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (IBP). IS Industry Solutions Solutions to cater for specific industries’ needs. It can be, that in these solutions there are traces of SD, MM, FI, HR modules with extended functionalities – in this sense, IS is an ERP. Example includes: IS Oil, IS Utility, etc SAP BI/BW Business Intelligence / Data- warehouse It is data warehouse solution. It works with SAP (i.e. ECC, CRM, SRM, IS) and non-SAP data. From SAP ECC perspective, it is a comprehensive way to access and integrate data. SAP BPC Business Planning & Consolidation It is an acquired software for Enterprise Performance Management (EPM). Specific area of focus includes budgeting, planning and consolidation. SAP IBPF Integrated Business Planning for Finance It is part of S/4 HANA Enterprise Management, to bring all FICO Planning into one embedded BW environment. It primarily include Cost Center Planning, Internal Order Planning and Project System Planning. Ariba® Ariba® It is an acquired software for procurement and sourcing. Concur® Concur® It is an acquired software for Time & Expense Claims. SF SuccessFactors® It is an acquired software for HR related activities. Hybris® (Suite) Hybris® It is a set of SAP CRM solutions, comprising of the existing SAP CRM solutions with the other SAP acquired software(s). The name Hybris is taken from the one of the acquired CRM software. The Hybris Family, as of writing, comprises of 5 solutions (Hybris Commerce; Hybris Billing; Hybris Marketing; Sales Cloud; Service Cloud)
- 13. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Business & Processes ERP Operations Introduction The purpose of ERP is to optimize the use of its resources (i.e. money, goods and people); to achieve this, the underlying ERP must provide information in a consistent and timely manner. Achieving the above would require a roadmap of clear policies and well-defined processes. There are well-known process terminologies, such as Order-to-Cash, Procure-to-Pay. Each of these will be looked into with details. The below diagram and narratives describe how each processes are inter-linked. ERP Core Processes
- 14. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less The ERP operations typically start with a customer order going through the Order-to-Cash process. Basing on the business model, appropriate supplying processes will be triggered. For a trading business model with stocked goods, simple inventory issues will be the process for supplying. For a trading business with non-stock goods, purchase orders will be raised to start the Procure-to-Pay process. For a manufacturing business, the Plan-to-Product process is used. The process comprises of the planning phase and the execution phase. Planning decision depends on whether it is using Make- to-Stock or Make-to-Order scenario. During execution phase, production orders will be raised to start the manufacturing steps. In additional, goods that can have preset variation requirements need to be processed via Configure-to-Order scenario. For a manufacturing business with complex product (for instance, pre-studies are required), a project step is needed prior to manufacturing. This flow is termed as the Engineer-to-Order process. For complex product that does not need manufacturing, the Build-to-Asset (aka Built-to-Order) process can be used; a project will be setup for detailed tracking, subsequently resulting in a final asset that may be sold. Financial accounting and management accounting will be managed through the Record-to-Report and Controlling process, respectively; whilst the human resource requirements will be managed though the Hire-to-Retire process. In summary, ERP empowers the enterprise to operate with seamless dataflow and business insights. Enterprise profitability and performance can tracked and presented, with transactional details that are readily available across the sub-ledgers and sub-modules. Note: in certain organizations, Plan-to-Product solely refers to Make-to-Stock scenario. However, for our purpose, the term will be used generically for both scenarios.
- 15. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less This section is not part of the preview
- 16. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less The CO Module Controlling Overview SAP CO is dealing with internal management reporting (aka Management Accounting). It deals primarily with 3 key aspects, namely: Cost Analysis, Budgeting, and Profitability. Controlling may deploy various applications for each of their controlling functions. To get a grasp of how these myriad applications work in symphony, it is helpful to know which controlling ‘departments’ (or job functions) works with each of the areas. For cost control there are the controllers; for profitability there are the FP&A (Financial Planning & Analysis) Analysts. Budgeting is somewhere shared. For Cost Analysis, controlling users do use the CO functionalities within their ERP, sometime supplementary cost data are extracted elsewhere. If the ERP is SAP ECC, then SAP CO mostly likely will be used, due to its intrinsic level of integration. Almost nobody with SAP ECC, replaces its SAP CO module and takes up something else – that is unimaginable. For Budgeting, users typically use specialized budgeting application(s) that differ from their ERP. This is because budgeting occurs at various levels (i.e. group, enterprise, operational) and multiple timeframes (i.e. long-term, short-term, micro-term). SAP do offers SAP ECC Budgeting sub- modules (Investment Management, Project Systems, Internal Order, and Cost Center) and SAP BPC to support ERP level Budgeting. SAP BPC is recommended if the enterprise is having both SAP and non-SAP systems as ERP.
- 17. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Controlling Solution In FI, transactions occur at the company code level; in CO, transactions are at the controlling area level. One controlling area can have multiple company codes; this allows cross-posting of cost/revenue among the Cost Objects. This is in line with FI statutory reporting requirement at company code level; and global management reporting. Depending on how the enterprise is run, the controlling area can be modelled at Company Code level, Regional level or Group level. In case, controlling area is modelled below Group level, the COPA operating concern structure can be implemented to further consolidate the controlling areas. In SAP CO, there are 3 primary sub-modules, namely: Overhead Cost Management (CO-OM), Product Costing (CO-PC), and Profitability Analysis (CO-PA). SAP PS can be used as part of controlling; whilst BPC is an alternate budgeting tool.
- 18. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Controlling Process: CO-PA SAP COPA is the sub-module that brings together all data at various levels and harmonizes it in the context of reporting profitability. It provides a unified reporting platform for Slice-and-Dice Analysis. There are two versions of COPA, namely: Vanilla (aka Account-based) and Costing- Based. Both versions are setup to provide enriched business dimensions for analysis. However, the degree of breakdown at the value level differs. The Vanilla version revolves along FI and is based on GL accounts (cost elements). Basically, it enriches FI postings with key information such as Customers, Products, Market Segments, Sales Order number, Purchase Order number etc. – while having fully reconcilable figures with SAP FI. It provides cost information at the total level (GL accounts/cost elements), without any COGS breakdown or Variance breakdown. Typically this is sufficient for non-manufacturing organization. For enterprise with complex requirements requesting details on the COGS and Variances breakdown; the Costing COPA, provides up to 120 freely-definable value fields to account for the detailed requirement of cost/revenue breakdown – while still allowing up to 50 analysis fields (aka dimension/characteristics). In addition, it also allows early posting of Sales Order entries prior to Billing into Costing COPA for Order Intake Analysis. The actual data in Costing COPA can be fed into production for Sales & Operations Planning (aka SOP).
- 19. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Costing COPA forms the foundation of Cost-of-Sales Reporting (COS). Cost-of-Sales typically breakdown Contribution Margin into various stages (at least 3), to get insights into various cost components and breakeven points. In the below, it is shown that Contribution Margin I deals with variable costs, Contribution Margin II deals with fixed manufacturing costs and Contribution Margin III deals with non-manufacturing costs. The postings into between COPA, CO and FI are well synchronized to be reconcilable.
- 20. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less The Budgeting Solution There are at least four approaches to budget control in SAP. Cost Center and/or Internal Order level: this is a small-scale approach within ECC. It is easy to setup and understand. However, budget is not centrally controlled, as budget is set at individual object types (i.e. CC, IO). Core budget controls include availability tracking with notifications and cost breakdown (budget/commitment/actual) reporting. Project Systems (PS) level: this is a comprehensive approach within ECC, where WBS is set as the budget object with costs are booked against it. Apart from core budget control, PS also allows hierarchical budget and cost management within PS. Refer to the earlier Build-to- Asset process in SAP PS. Fund Management (FM) level: this is a holistic approach within ECC, where fund objects (i.e. Fund Centers, Fund Programs, etcs) are set as the budget object whilst costs booked against FI / CO are relayed to FM. Apart from core budget control, hierarchical budget management of all cost object types is possible at FM level. It also offers cash availability view, which is not possible with CO. SAP BPC: this is an external SAP system from ECC. BPC is both a budgeting and consolidation system; if budgeting is done at BPC, the budget itself can also be consolidated and match against actual consolidation figures.
- 21. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Within ECC options: Budget control setup revolves among cost objects that can hold both cost and budget (i.e. CC, IO, and WBS). If in-depth capital investment management and Asset Accounting integration is required, the Investment Management (IM) component can be further activated. In the case where CO budget control is not covering the full budgetary requirements, the Fund Management (FM) component can be activated. Actual budget consumption instinctively comes from procurement (i.e. PR, PO). Other sources can be manual FI / CO transfers. SAP budget control takes into consideration of actual cost and commitment. When a PR is approved, it starts to hold a commitment; this consumed a portion of the allocated budget for the specific cost object. When the PR is converted to a PO, the budget is released from the PR but held at the PO level. When the PO is fully delivered or final invoiced, the commitment is closed, and actual cost takes place. At any moment of time, cost and commitment held by various objects are traceable.
- 22. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less If FM is activated, then the budget control is maintained at the funds objects (instead of cost objects). Individual cost objects will be tagged to a fund objects (e.g. Fund Center, Fund Program). GL accounts will be tagged to a FM commitment items. The combination of fund object and the commitment item will hold the budget. Budget control at FM level has various versatilities, such as budget control across modules, hierarchical budget management, revenue-increasing budget and cash availability view. As FM is more to cash-basis whilst CO is more to accrual-basis, there will be consumption categorizing differences. In FM, down-payment invoice is treated as commitment while CO it is not monitored. In CO, goods receipt (valuated) is treated as actual while cash-basis FM may not. Unlike CO, consumption can be mapped into FM without CO assignment (e.g HR-to- FM).
- 23. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Using SAP BPC: SAP BPC is highly integrated with ECC. It can extract actual data from ECC for planning, and push budgeted figures into ECC for fund control. Its user interface is Excel-based; and provides various new add-in excel formulas for users to work with. BPC can be utilized as the centralized planning platform for the whole of ECC. This ensures consistency of user input – rather than using various planning utilities in each ECC modules. Collectively, the business functions (i.e. HR, Project & Engineering, Finance & Administration, Sales & Distribution, and Production & Procurement) can centrally perform Manpower Planning, CAPEX & Deprecation Planning, Finance & Administrative Planning, Sales Forecast, Purchase Forecast, etc.
- 24. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less The BPC-ECC Budget & Planning Process (1). BPC will extract the actual data from FI/CO/AA via nightly job. (2). Business divisions/functions users input value for planning and forecasting using the BPC Excel interface. (3). Actual and Plan data can be compared side-by-side. (4). The planned data can be used for centralized consolidation. (5). The planned data is then retracted into ECC (FM) - for Budget Control. BPC layout is well suited for customized planning process. For instance, if the budget cycle starts in September with remaining 3 months (October, November, December) as forecast and next 12 month (January to December) as planned – the whole 15-month cycle can all be achieved in one excel layout. As BPC leverages on the processing power of SAP BW / HANA, it can offer real-time what-if analysis.
- 25. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Enterprise Architecture An enterprise is supported by myriad of applications for its business execution and strategic planning. This goes from its production shop floor with MES (Manufacturing Execution System) to its ERP to its headquarters’ EPM (Enterprise Performance Management) system. ERP is the central piece of software in the Enterprise Architecture (EA). It is the nerve center of information, taking data from various sub-systems, and setting the basis for management planning. From an enterprise perspective, it is important to strategize on what application capabilities to acquired, and how should each of these applications be used. Apart from knowing the ERP modules, it is important to know how each of these modules is connected to its corresponding sub-systems. ERP Core with Potential Integrative Sub-systems
- 26. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Complementary components used by the industries
- 27. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less An Enterprise Architecture should, in general, be able to handle upstream demands from customers agilely, collaborate with suppliers readily, process high-volume invoicing/payment efficiently, operate its internal processes effectively, and analyze its data near-realtime - perhaps with a centralized ERP and/or mixed specialized applications. CRM suites enable enterprises with capabilities such as extensive pricing, quotation, service and analytics to handle varying upstream demand. The potential CRM can be SAP Hybris suite or Salesforce. In addition, CRM-related Billing solutions are able to track and bill large numbers of customers, while reducing posting footprints into ERP. Likewise, in financial institutes, large number of financial assets can be processed in SAP FAM (Financial Asset Sub-ledger) before having the net balances sent into ERP. SRM solutions (such as SAP SRM, Ariba) enable enterprises to have access to market-aligned practices, while maintaining good collaboration with suppliers. For backend high-volume invoice processing, OCR (Optical Character Recognition) solutions, such as WMD xFlow and OpenText VIM, can be deployed for automated scanning (into ERP) – this free up the effort for human processing and errors. For high-volume payments and collections, bank integration can be setup using EDI/XML/CSV formats. Online self-service tools (such as Concur Claim, SuccessFactors, Taleo, Workday) can be deployed, to ease the administrative load. For advanced planning and scheduling of production, SAP SCM or other best-of-breed alternatives (such as i2 and Manugistics) can be deployed for an end-to-end supply chain solution. Specialized engineering software (such as CIDEON PDM Drawings, Maximo Asset Management) can be used to further enhance the product design and engineering architecture. External project management tools that are more compatible to the MES chosen (such as Primavera) can be brought into ERP or PPM for holistic analysis. The demand for Enterprise Performance Management, exist even without an ERP in place, matured applications such as SAP BPC, Hyperion Planning, Cognos TM1 can be used integratively or without. Business Intelligence tools such as SAP BusinessObjects, Tableau, Qlikview, PowerBI, can used to facilitate visualization and trends identification.
- 28. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less The Enterprise Architecture varies with the industry that the enterprise is in, as such the ERP modules activated per industry will be different. We will explore various architecture deployed using examples from the Engineering, Real Estate, Retail and Banking industries. Sample Architecture of Commercial Banking Enterprise
- 29. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Why a Bank would require an ERP? Banks have 101 trading applications, literally. All these systems need to be consolidated into the General Ledger for regulatory reporting. With all the data available in the ERP, true hedging and in-house cash can be utilized. It is only in the central reporting system, Balance Sheet items can be netted as either an asset position or a liability position. In a Banking organization, there can be Commercial Banking and Retail Banking scenarios. Financial institutes deal with financial instruments (such as trade finance, debt, securities) as products, rather than physical goods. The central module used would be FI, and CO; while a myriad of trading applications becomes its sub-ledgers and sub-modules. The specific challenge of this industry is stringent regulatory requirements for financial assets, hence it is recommended to take up Financial Asset Sub-ledger (FAM) to meet the data granularity requirements of IFRS 9. For commercial banking, there can be a variety of trading (or loans) systems used. Hence, the Enterprise Architecture needs to include a layer of data harmonizing process before entering the SAP ledgers. FAM is highly ECC compatible and has functions that support the liquidity coverage requirements. In the event that FAM does not fit the Enterprise Architecture schema, a custom application can be used to meet the intricate needs of Risk Weighted Asset Model. For retail banking, it is recommended using Industry Solution for Banking (IS-B) for a smooth integration. It is known that Deutsche Bank, for example, has been using ECC for years to consolidate its high volume of financial transactions.
- 30. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less This section is not part of the preview
- 31. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less Customization Concept As ERP caters to a wide range of business scenarios, its standard processes could not be fine- tuned to the enterprise’s needs in every way. This means customization is inevitable. But to what extend? Customization is a double-edge sword: on one hand it allows tailoring of ERP components to the specific enterprise business; on the other it introduces variation processes against the standard ERP processes. Variation processes are not necessarily bad, but it might have compatible issues with the ERP (especially during upgrades). Hence, an optimal balance needs to be established between customization and standardization. There are 6 identified customization areas – abbreviated as RICEFW: (1) Reports: This is for custom reports to meet the individual enterprise reporting needs. Each enterprise belongs to a different industry and business environment, its needs for reporting differs. ERP typically provide various reporting utilities for customized reports. For SAP, there is the Report Painter tool for fast report generation in finance; whilst various Logistic Information InfoStructures are available for logistic reporting – in both case there is no need to resort to programming. SAP Infoset Query builder can be used to join data from both finance and logistics via its click-and-drag interface; programming codes may be inserted to various spots for enhanced querying. Extended reporting can be performed using SAP BW/BI. S/4 HANA provides HANA modeling capabilities for extract analytical data in-place. (2) Interfaces: This is for interfacing connectivity to meet the individual enterprise application landscape. Each enterprise has different applications infrastructure, its needs for integration differs. ERP will not know beforehand what these exact requirements are but may offer adaptors for smooth interfacing. In logistics, it is possible to have integration with external vendor or even internal vendor for order automation. In finance, it is common to have bank interfaces for automatic bank transfers. SAP provides various pre-built interfacing mechanisms for logistics and finance. Interfacing technologies include CSV, XML, EDI, SAP-ALE, SAP-IDoc, Web Services, etc. At the frontend level, it is also possible to use external user interfaces coded in C++, Java, Excel or even Python. (3) Conversions: This is for bringing in legacy data into the ERP. SAP uses the Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW) tool to load legacy data to standard objects. Data can be prepared in an Excel file, and the LSMW will run through each record while data-posting into specific transaction screens. Custom LSMW can be built. (4) Enhancements: This is for adjusting standardized ERP processes. Each enterprise will have its idiosyncrasies in its business processes, certain level of alteration is required. SAP provides various enhancement techniques (such as Exits, BADI, BTE, Spots, etc.) for business alignment. For example, the ‘Selling Type’ information needs to be captured in the Sales Order. Hence, there is a need to create the ‘Selling Type’ input field in the Sales Order screen using Screen Exits. During saving of the Sales Order, the ‘Selling Type’ is updated to the database - using Program Exits.
- 32. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less (5) Forms: This is for custom forms to meet the individual enterprise correspondence and documentation needs. SAP provides template forms (such as Billing Invoice, Dunning List, Picking List) for enterprise to adapt for usage. (6) Workflows: This is for automated tasks and notifications. SAP provides predefined workflows (such as PR/PO approval). Custom workflow can be built.
- 33. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less The Next Frontier The development of ERP is influenced by two primary factors: Business requirements and IT capabilities. This has resulted in ERP reinventing itself. An example would be the next generation ERP, S/4 HANA Enterprise Management (S4EM). It leverages on its high performance in-memory capabilities to eliminate architectural limitations and simplified its data model – this entails greater ease and elegance for handling new requirements such IFRS 15 and IFRS 16. The fundamental change of S4EM is to have a centralized ledger structure, aka the Universal Journal (UJ). In ECC, a posting in FI, may lead to a posting in CO. Hence, at least two documents are being created in two places. With UJ, postings are only passed once into one place. This ensures high degree of data synchronism.
- 34. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less End of Preview ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less https://www.amazon.com/dp/B083C3X8YY This disclaimer informs readers that the views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in the text belong solely to the author, and not necessarily to the author's employer, organization, committee or other group or individual. The author is not affiliated, associated, authorized, endorsed by, or in any way officially connected with SAP®, Oracle® and Microsoft®, or any of their subsidiaries or their affiliates.
- 35. ERP Made Simple: ERP Explained in 80 Pages or Less tags: #bestpractice #mindmap #transformation #financetransformation #fiori #fiori3 #cloud #onpremise #asap #activate #activatemethodology #sapcloud #saphec #sappaas #sapsaas #sapasap #sapactivate #sapmigration #sprint #ocm #bpr #bpm #businessprocess #erp #mnc #sapb1 #businessone #bydesign #oracle #oraclefusion #peoplesoft #siebel #jde #jdedwards #netsuite #sage #infor #d365 #dynamics #hana #saphana #s4hana #sapinmemory #hanamodeling #soh #universaljournal #profitabilityanalysis #marginanalysis #acdoca #matdoc #prcd_elements #ico #transferpricing #pricing #costing #productcosting #standardcosting #actualcosting #materialledger #ibp #bpc #hfm #bw #epm #cpm #hyperion #essbase #tableau #powerbi #businessobject #lumira #cognos #qualtrics #maximo #primavera #vim #xflow #salesforce #hybris #ariba #concur #successfactors #taleo #cashmanagement #creditmanagement #fundmanagement #bcs #budget #downpayment #collection #dispute #riskmanagement #ihc #trm #treasury #liquidity #bank #bankmanagement #controlling #depreciation #assetaccounting #projectmanagement #projectsystems #wbselements #investment #o2c #p2p #r2r #h2r #fscm #scm #mrp #crm #fico #sdmm #mts #mto #eto #mrp #copa #copc #coom #apar #balancesheet #profitloss #margin #wbs #budget #commitment #payroll #financial #accounting #financialaccounting #subledger #ccm #poc #gaap #ifrs #ifrs16 #ifrs17 #ifrs9 #consultant #ams #tutorial #career #goal #mnc #finsc_ledger #okkp #okkn #ka01 #ks01 #obk9 #s_alr_87013611 #ksb1 #ksb5 #kvbi #cji3 #kob1 #fmderive #oby6 #coois #md01 #md04 #cs01 #ca01 #cr01 #co01 #iw31 #cogi #co11n #cm21 #opl8 #ck11n #ck30n #ck3m #ckmlcp #kkax #kkao #cj88 #ko88 #va88 #kedr #ke30 #gr55 #oktz #kzs2 #opsa #cj20n #cj30 #ob08 #ob09 #s_alr_87012284 #s_alr_87012357 #s_p00_07000134 #tax #vat #gst #withholdingtax #oby6 #fs00 #fss0 #fsp0 #fb50 #fb50l #fb01 #fcv #fagl_fcv #fagl_fc_val #fbl1n #fbl5n #fagll03 #fbzp #fi11 #f110 #s_alr_87011990 #ftr_create #ftr_edit #as01 #afab #aw01n #ar01 #ao90 #oayz #oaoa #va01 #vf04 #vf11 #vk11 #vov8 #vtaa #vkoa #vofm #ome9 #mm01 #omx1 #omx3 #oms2 #omjj #me21n #migo #miro #mr8m #mmbe #mb52 #obyc #pa03 #pa40 #se30 #se38 #se80 #se37 #sq01 #eclipse #hanastudio #admp #sgl1 #st22 #sm20 #st01n #pfcg #grc #rpa #togaf #cobit #pmp #itil #agile #scrum #ricef #lsmw #bd10 #bd87 #spro #img #c_tfin #c_tscm #p_s4fin #c_ts4fi #c_ts4co #c_ts420 #c_ts450 #c_ts460 #sapjob #sapcertified #sapcertification #developer #abap #java #django #python #github #jira #programming #fullstack #edi #idoc #modelcompany
